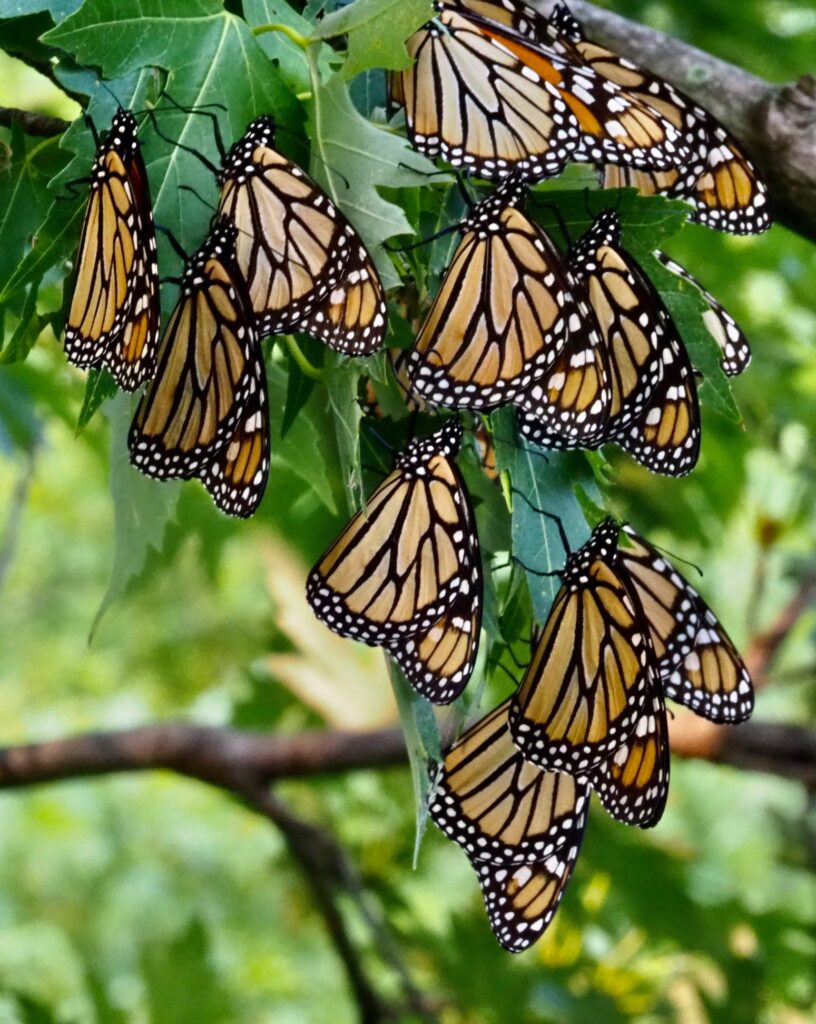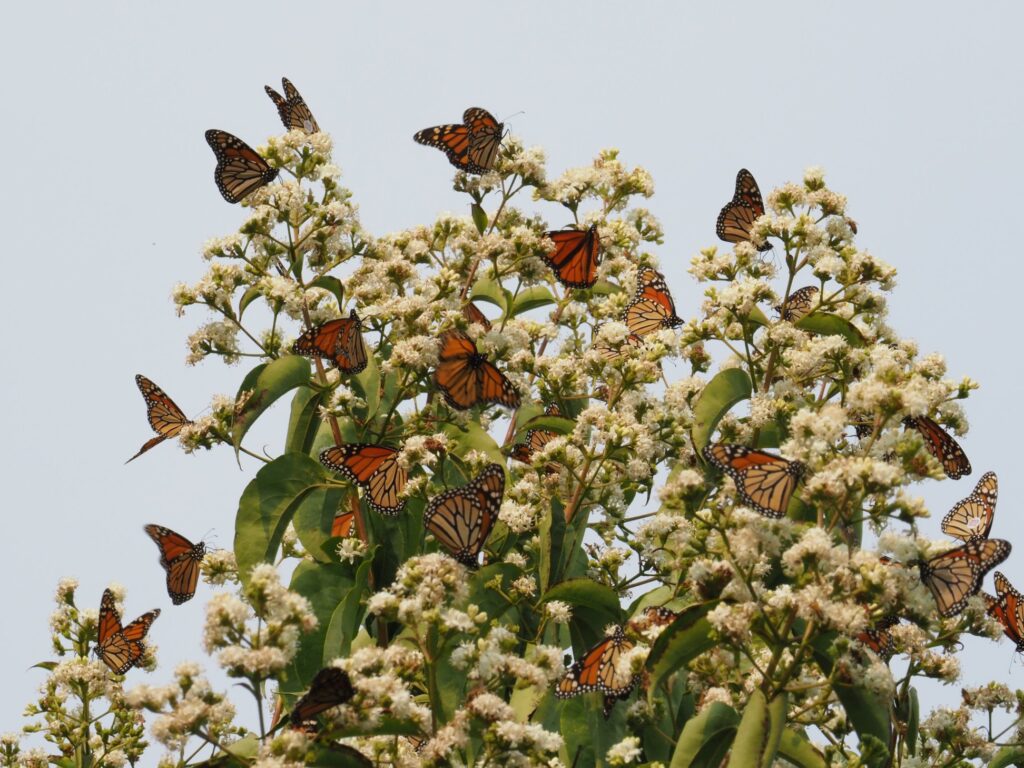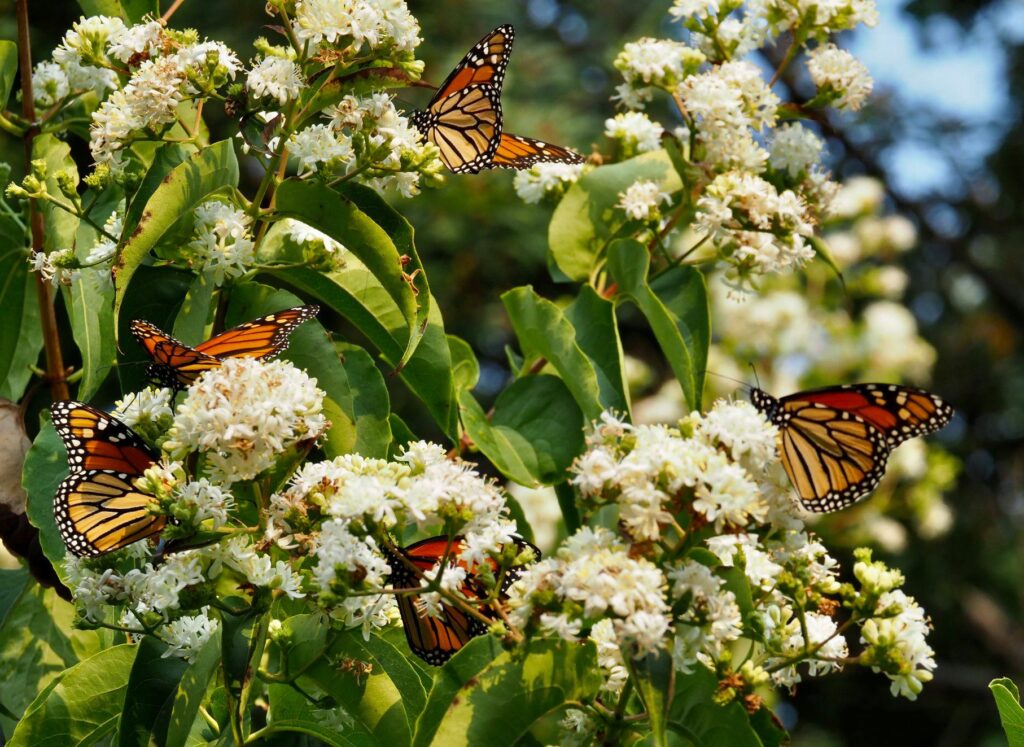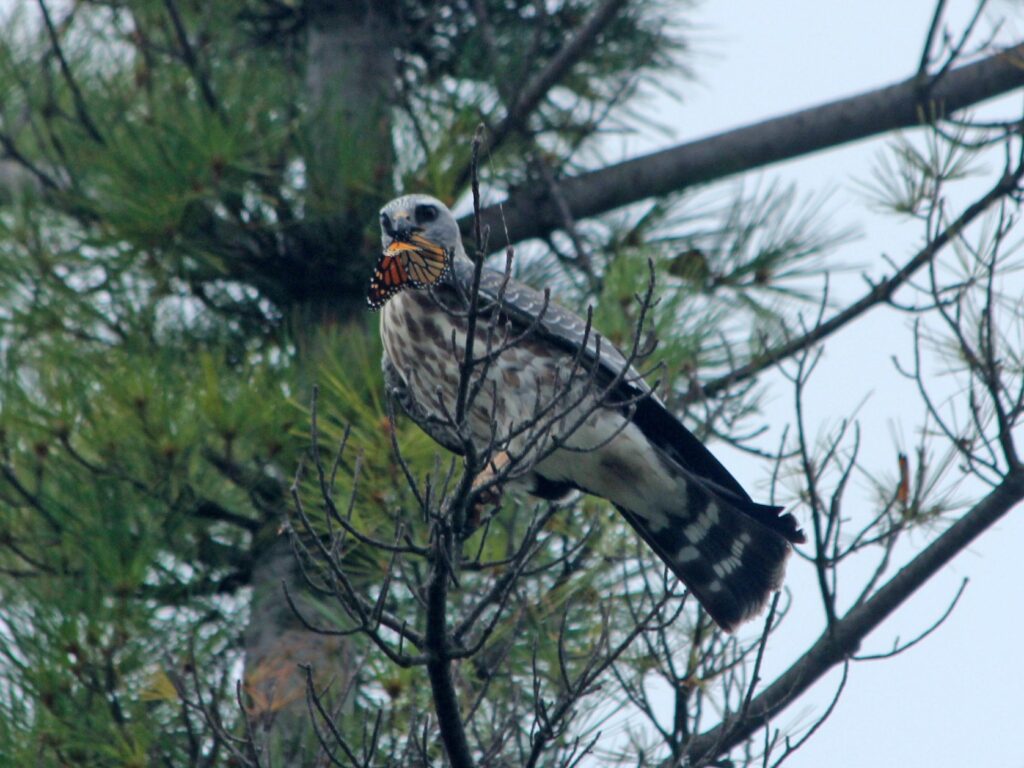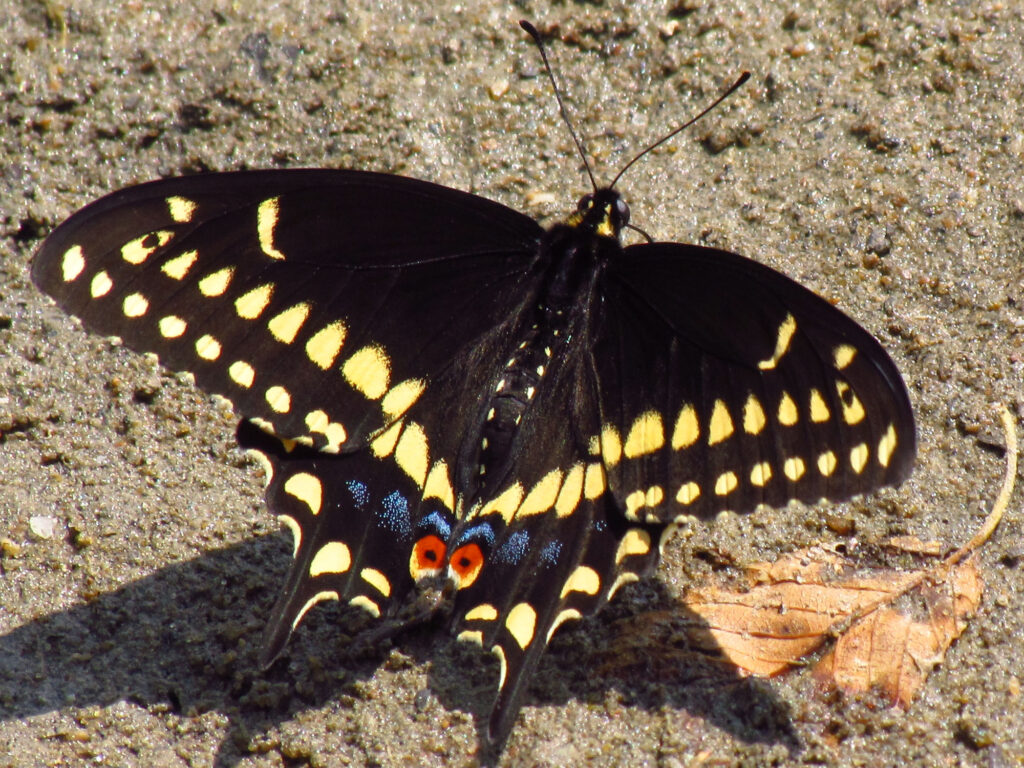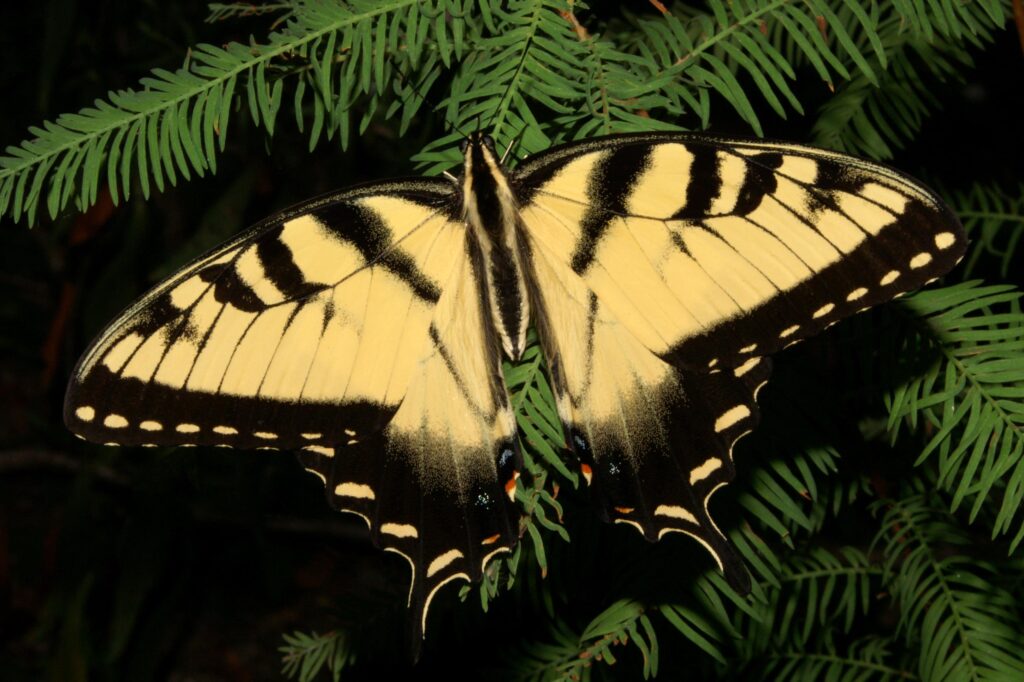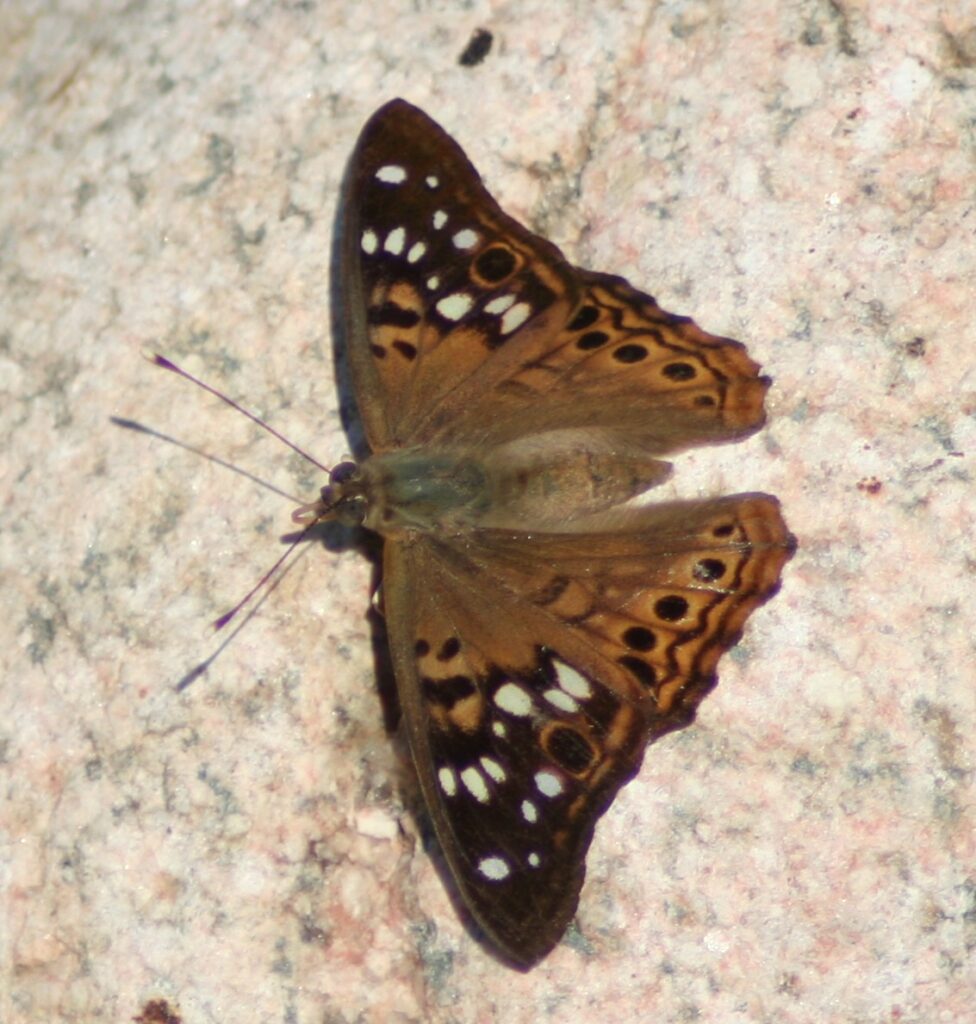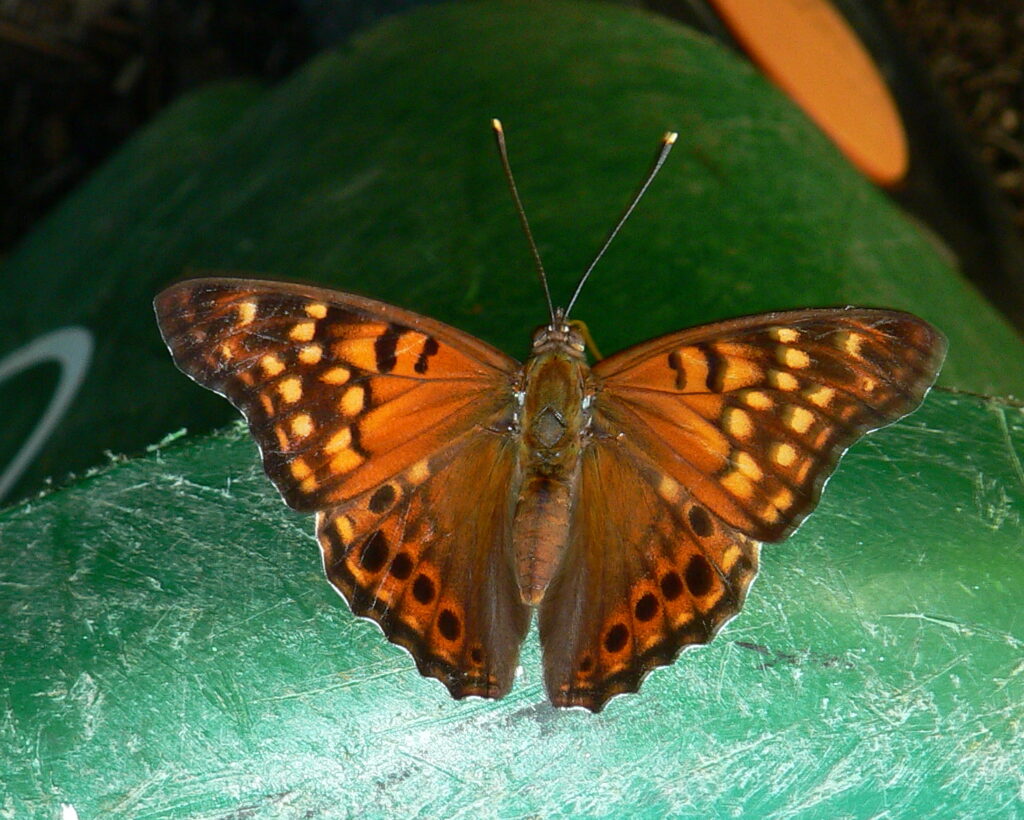
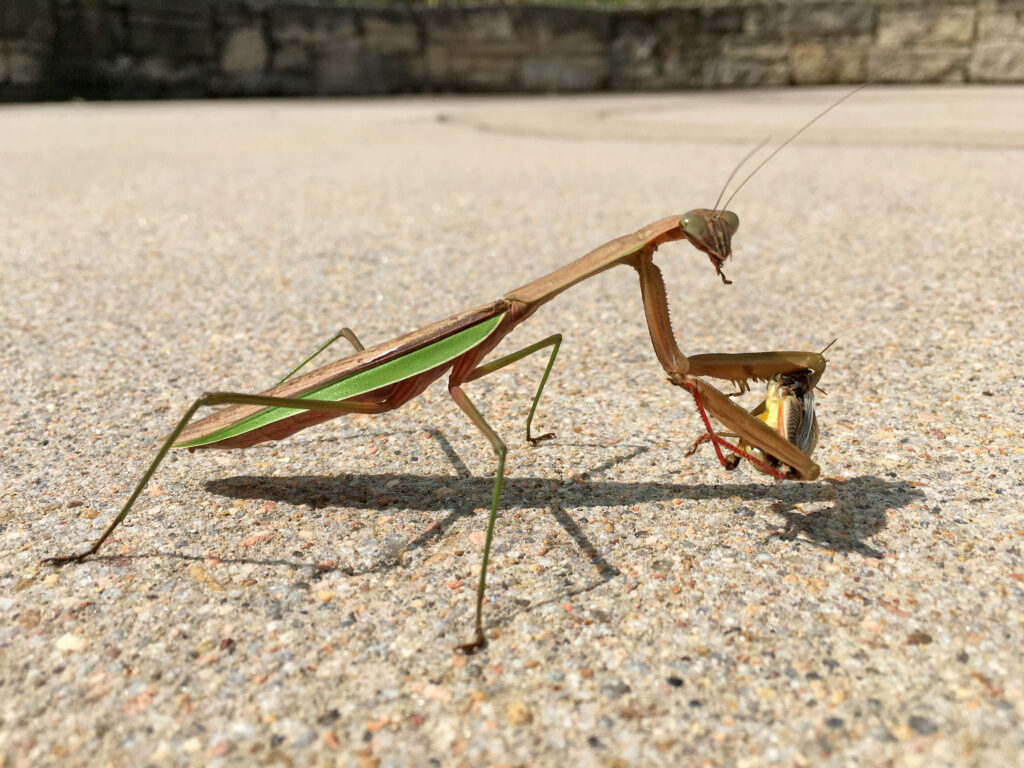
The praying mantis is a medieval-looking predator of the garden that could just as well be a source of a horror film. Females are known to bite the head of their male partner during copulation to prevent his premature flight and then proceed to eat him after his job is done. If newly-hatched nymphs don’t find enough insects to eat shortly after leaving the nest, they start cannibalizing their own siblings. After watching my grasshopper-eating video at the end of this post, even some meat-eaters may swear off KFC for a very, long, time.
Identification
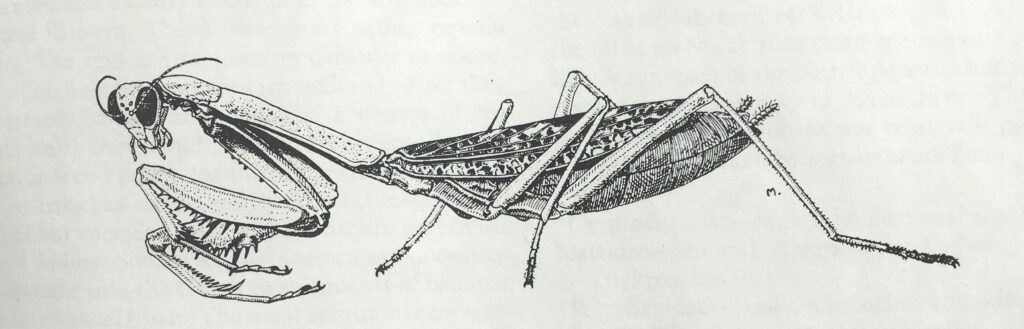
Praying mantises or mantids have compound eyes in freely moving heads on a pronounced neck and are the only insect that can “look over their shoulder.” Their front legs are muscular viselike appendages with spines held in front of them. They lie in wait, ambush their prey, and then hold and eat them alive.

Kansas has five different species of mantids. There are three native species and two introduced. Of our native species, two are small, uncommon, typically found in prairies, and described in Insects in Kansas (Salsbury and White) as follows:

For the remaining more common three species in Kansas (Carolina mantis, Chinese mantis, and European mantis), the following is a description of each provided courtesy of Missouri Department of Conservation (mantids) with bugguide.net links to photos of each individual species:
- Carolina mantis (Stagomantis carolina). Native.
- Pale green to tan or mottled gray
- Adult length 2–2¼ inches
- The combined length of the head and thorax is about as long as the abdomen.
- The middle pair of legs are about twice as long as the antennae.
- Females are essentially flightless, as their wings are relatively small — when folded, they do not extend as far as the abdomen tip; usually only about three-fourths of the way down the body.
- Males may have the wings extend beyond the abdomen tip and may fly to lights at night.
- There is a black patch on the outer pair of wings.
- Examine the facial shield (the part of the face in front of the antennae and between the eyes: in this and other Stagomantis species, it is long and narrow (in the Chinese mantis, it is fairly square and has vertical stripes).
- Egg cases are somewhat flattened, elongated, teardrop-shaped structures.
- Chinese mantis (Tenodera sinensis). Nonnative. Very commonly encountered.
- Tan to pale green; tan individuals often show a stripe of pale green on the side (it’s the borders of the green front wings)
- Adult length 2¼–4 inches or more
- Examine the facial shield (the part of the face in front of the antennae and between the eyes): in the Chinese mantis, it is fairly square and has vertical stripes (in our native Carolina mantis, it is long and narrow and lacks stripes).
- Flies well, often attracted to lights at night.
- Egg cases resemble tan toasted marshmallows. They are fairly round, about as long as wide, Ping-Pong-ball size; usually attached to twigs of bushes and small trees.
- Native to east Asia. Introduced to North America accidentally in 1896. Later, imported on purpose in hopes of combatting insect pests. Among the many insects it consumes are our smaller native mantids, and it may be playing a role, in some regions, in the declining populations of the Carolina mantis. Because the Chinese mantis has been widespread in our country for so long, it is difficult to determine what its ecological impact has been on native ecosystems. Because of the females’ large size, they have occasionally been recorded eating small vertebrates, including small reptiles and amphibians and even hummingbirds, but these seem to be relatively rare occurrences that do not have a significant impact on populations of those species.
- European mantis or praying mantis (Mantis religiosa). Nonnative; probably the least encountered of these three.
- Yellowish green, cream-colored, or tan.
- Adult length 2–3 inches
- Diagnostic feature is a round black dot on the underside of the basal joint (coxa) of the forelegs. Sometimes this black dot has a white center. This spot can be hard to see when their “arms” are held together.
- Egg cases are rather egg-shaped, distinctly layered structures.
- Native to Europe. Introduced to North America accidentally in 1899. Later, imported on purpose in hopes of combatting insect pests. People may still introduce them occasionally.
For a visual comparison of the ootheca for these three species, HERE is an article with photos.
Reproduction
Once the female has been fertilized and consumes the male as a “last supper” of sorts, she develops and deposits her eggs to complete the life cycle before dying herself.

The female mixes the eggs with a frothy, protein-based material called spumaline and extrudes them onto a stem or building. This mass hardens to form a strong Styrofoam-like casing or ootheca that helps keep up to 200 eggs from drying out over the winter.
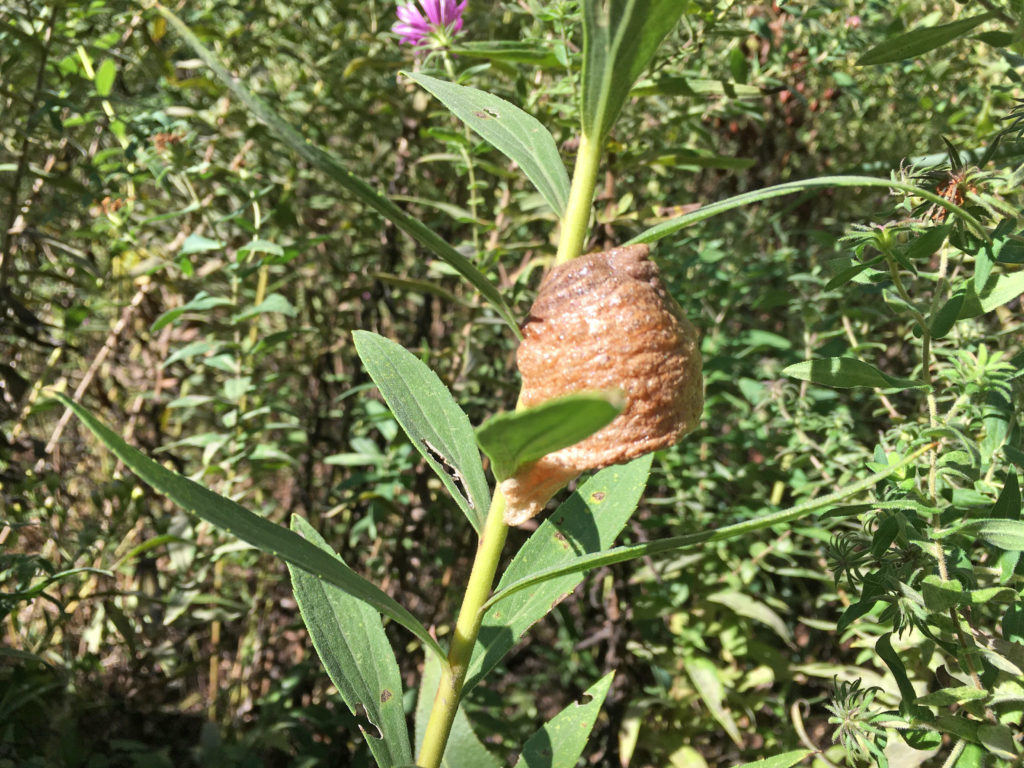

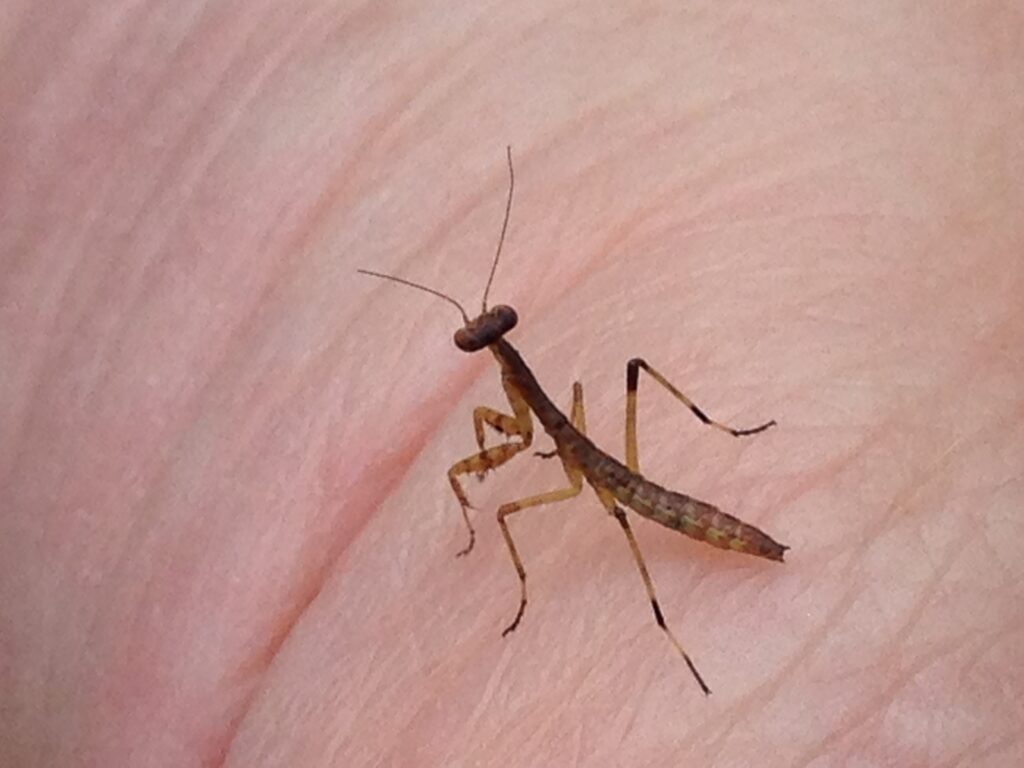
The nymphs that emerge from the ootheca in spring do not have different-looking larval stages like many other insects. They resemble adult forms throughout their entire juvenile development.

Biological Control
It would seem just as appropriate to name this creature the “preying” mantis. I have seen many instances of mantids munching on moths, butterflies, bees and more and recently captured video of a Chinese mantis eating a grasshopper (see end of blog).
Mantids are touted as biological control agents to get rid of pest insects in gardens and greenhouses. However, the effectiveness of this approach is questionable. While they efficiently prey on insects, a small release of mantids cannot possibly control all the insects that humans consider to be crop pests. Complicating their effectiveness, mantids also indiscriminately consume insects that we consider to be beneficial pollinators as well. And since nonnative mantid species are those most commonly distributed for biological control, some rightfully worry about the impact their continued introductions may have on smaller native mantid populations.
However you find and observe mantids in gardens and natural areas around you, observe and enjoy the habits of these fascinating creatures.