Due to the diligent nursery work of our suppliers, and a bit of searching on my part, we will have interesting new species to offer at our fall FloraKansas event, as well as some old favorites that have been missing from our inventory for awhile. We love to offer an ever-widening selection of hard-to-find natives to plant enthusiasts in our area!
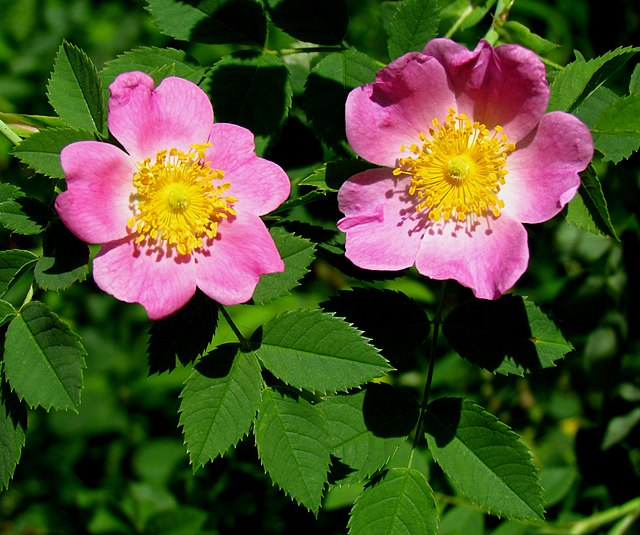
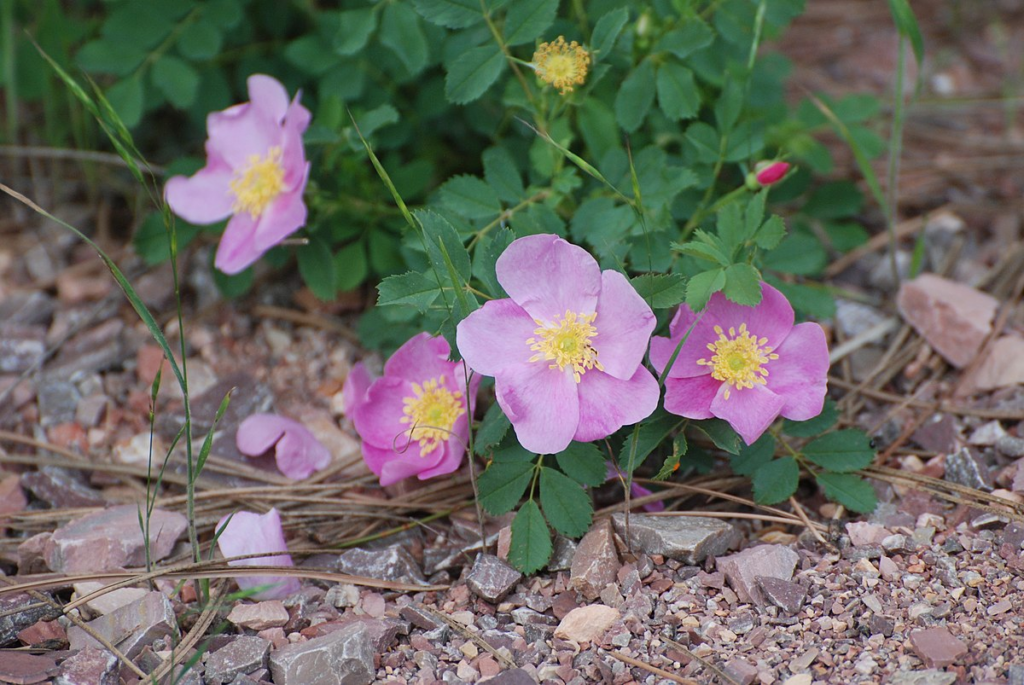
Rosa blanda
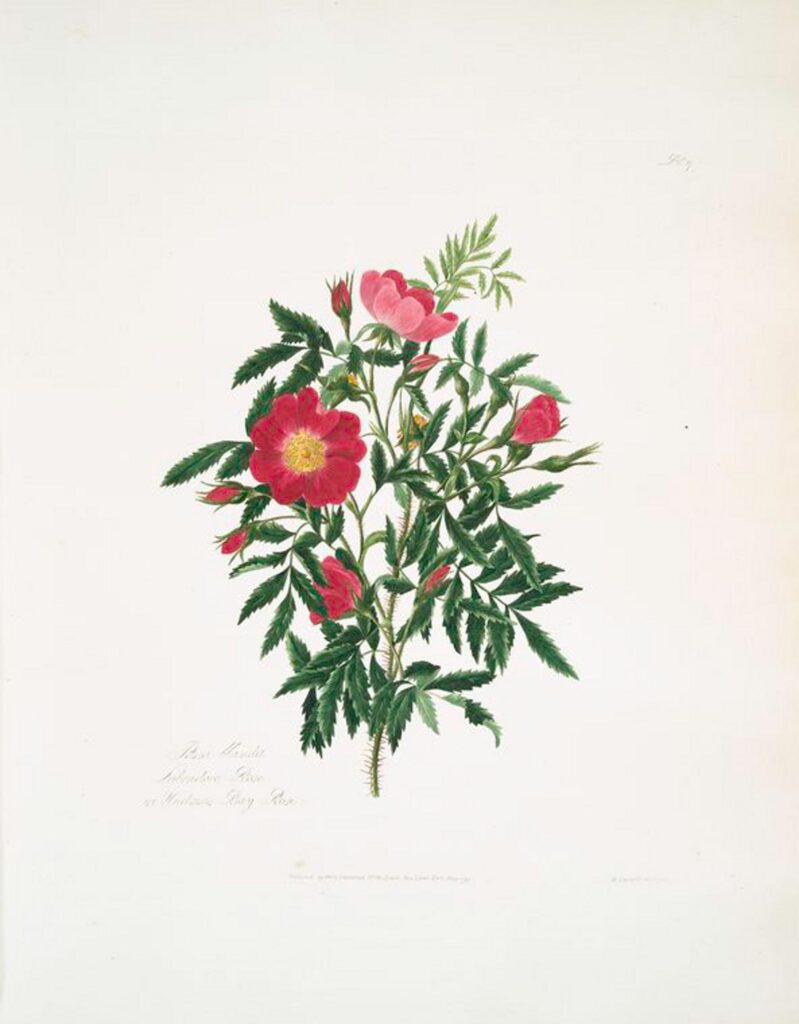

Smooth rose is an easy-care native rose found in pastures from Canada to Maine and as far southwest as Kansas. Grows in clay, loam or sandy soils and likes full to part sun. Nearly thornless, this rose is much friendlier than other roses with just a few prickles at the base of older stems. Light pink blooms are visited by bees, and the rose hips of fall are eaten by various forms of wildlife.

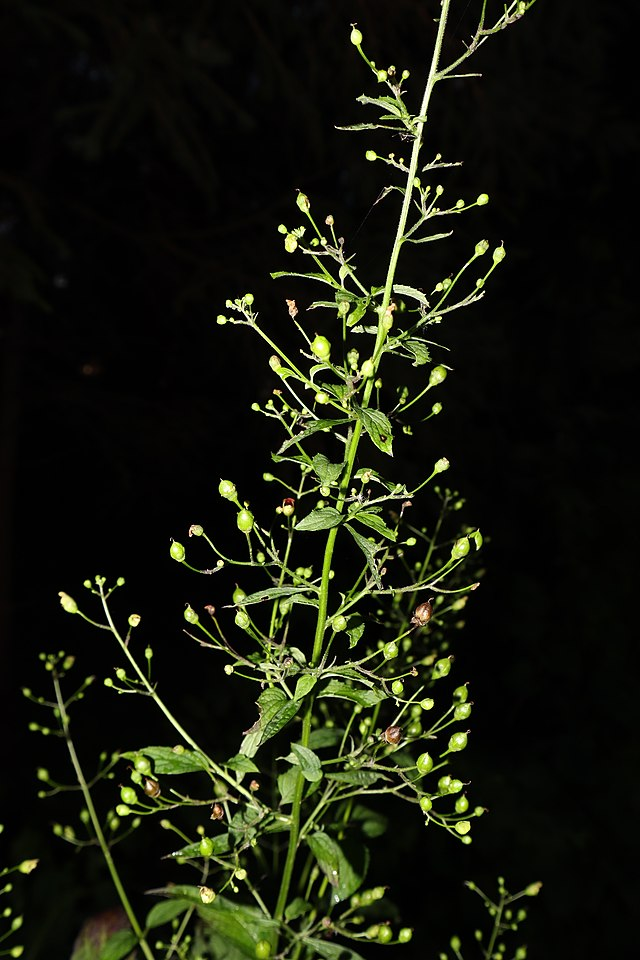
Scrophularia marilandica
Since its blooms are small and unassuming, you may have never noticed S. marilandica. I hope that changes! Figwort is tall with a many-branched flower spike. It is a boon for pollinators, and though it may seem spindly and weak its impact for bees is anything but. Native to the eastern third of the state and throughout the eastern US, it likes part sun to shade and a medium to moist soil.
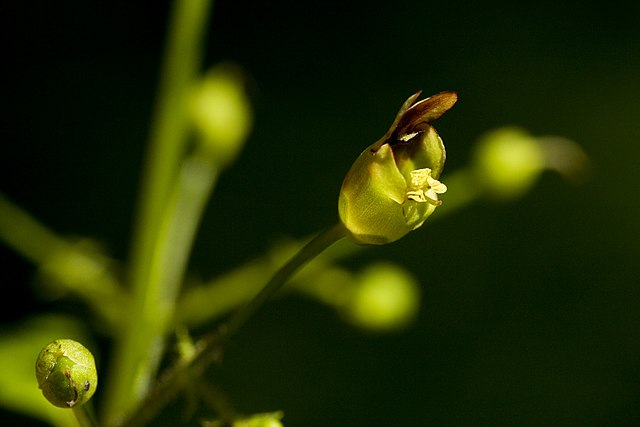

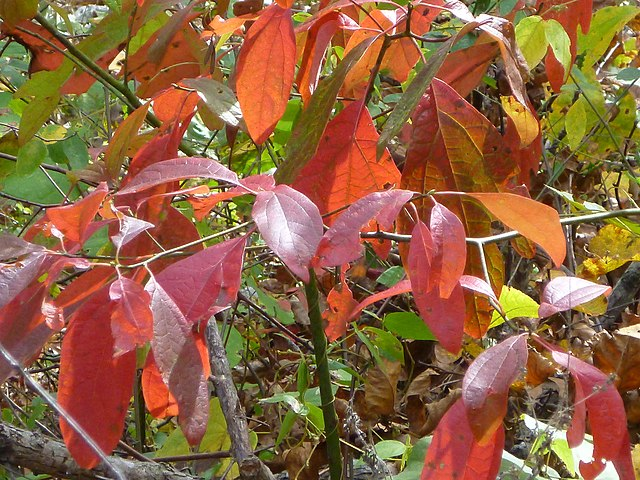
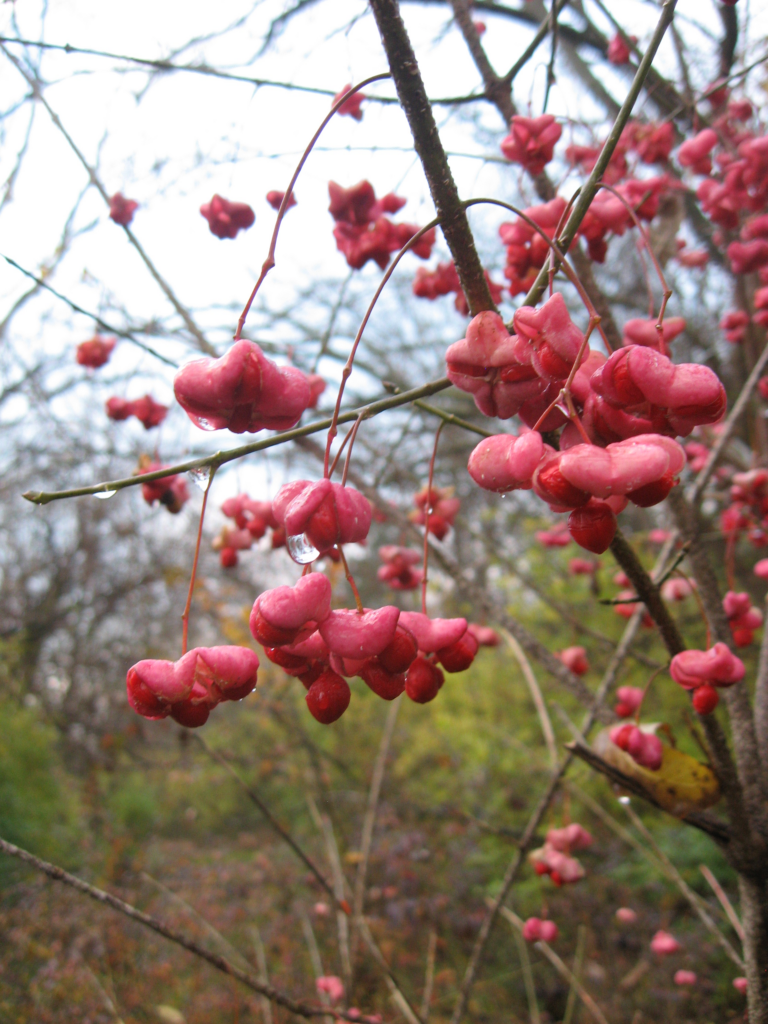
Euonymus atropurpurecens and Sassafras albidum
These two trees have a lot in common: they have vibrant red fall color, they thrive in partial shade and moist soil, and are native to the eastern US. As we are on the edge of their native range, they need extra watering through the Kansas summer.
There are lots of nasty invasives with the name ‘Euonymus’, but described here is the native North American species. Also known as Eastern Wahoo this small tree grows 8-10′ tall in our area, sporting burgundy spring blooms and lantern-like fruits in fall.
Sassafras fits into similar landscaping situations, though it can get a bit larger. In ideal conditions it can be 60 feet tall, but on dry upland sites here in Kansas it will commonly grow to 15-25 ft. There is simply no match for its fall color and lovely variable leaf shapes. Both of these woody species form suckers if happily situated. Be prepared to mow around them or let them spread into a grove.

At our fall FloraKansas event next week we will also have Bladdernut trees (Staphylea trifolia), Chickasaw plums (Prunus angustifolia) and Prickly Pear Cactus (Opuntia macrorhiza). I am excited to add these species to our growing list of natives for the plant lovers of central Kansas.
Are there plants you wish you could purchase but can’t find them anywhere? Please send us your requests and we will seek them out for future years of FloraKansas.