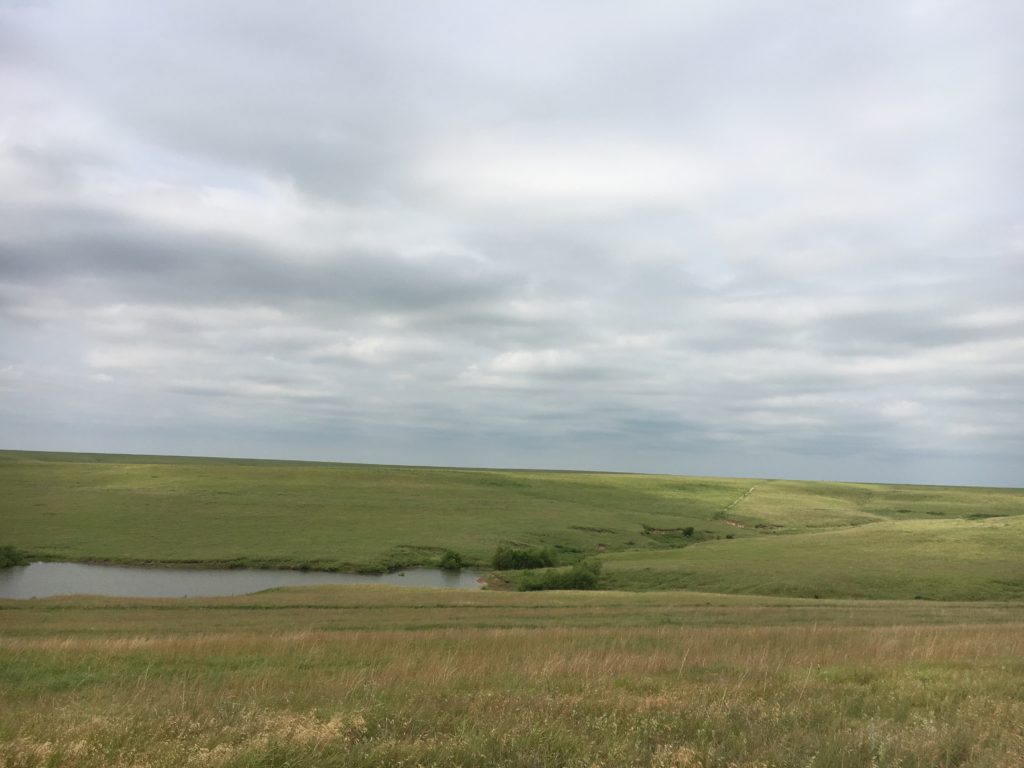
Terry and Carolyn Schwab live on 109 acres in Eastern Harvey County affectionately known by a former neighbor as the “Foothills to the Flint Hills.” While much of the county land has been converted to cropland over the last century, the Schwab property has remained in remnant prairie.
We received a grant in 2004 to identify and study more than 100 prairie remnants in South Central Kansas and to collect seed for our 18-acre Prairie Window Project prairie reconstruction project on-site at Dyck Arboretum. Until 2010, this work helped us develop a prairie landowner network through which we consulted with landowners and assisted them with their prairie management needs. It was during these years that I had the pleasure of first meeting the Schwabs. Ever since I have enjoyed observing the dedication they bring to being prairie restorationists and natural area enthusiasts.

Increasing Wildlife Diversity
The property was a moderately overgrazed cattle pasture when they acquired it in 1993. The Schwabs’ main goal as land stewards was to increase wildlife diversity through improved habitat and enhance their avid hobbies of bird-watching and fishing.
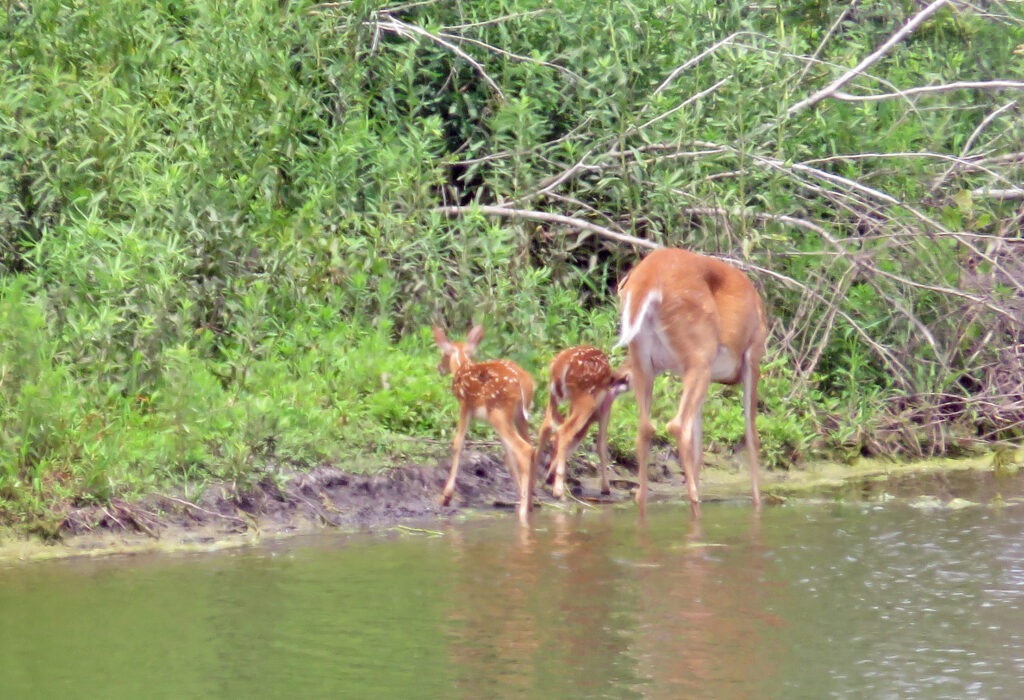
The remnant prairie and emergent wetland above and around the ponds on their land can consist of hundreds of species of grasses, wildflowers, sedges, and shrubs. High plant diversity translates to high wildlife diversity. Maintaining diverse herbaceous vegetation also serves as a good surface water filter that improves pond health. Terry and Carolyn knew that without grazing or other forms of grassland management, invasion of a handful of tree species (including nonnative species) would create a dense, and comparatively lifeless, forest canopy within decades. Plant species diversity would decrease and wildlife habitat would suffer. They needed to become prairie restoration land stewards.

Vegetation Management
Controlling woody species and removing nonnative wildflowers became top priorities for the Schwabs in their quest to improve wildlife habitat on their property. Their initial efforts were extensive and laborious. They cut Osage orange and eastern red cedar trees and manually dug out musk thistle. To maintain water levels in the ponds, they repaired holes in the dams and removed trees whose roots can compromise dam life.
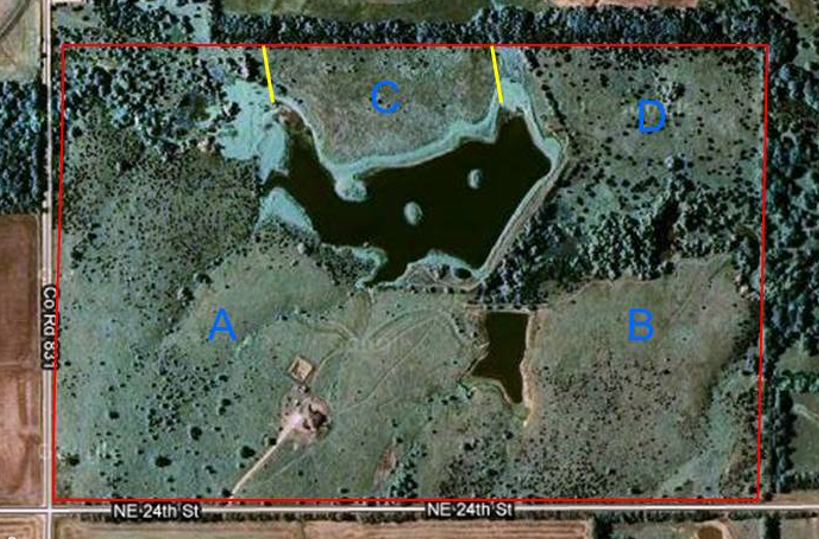

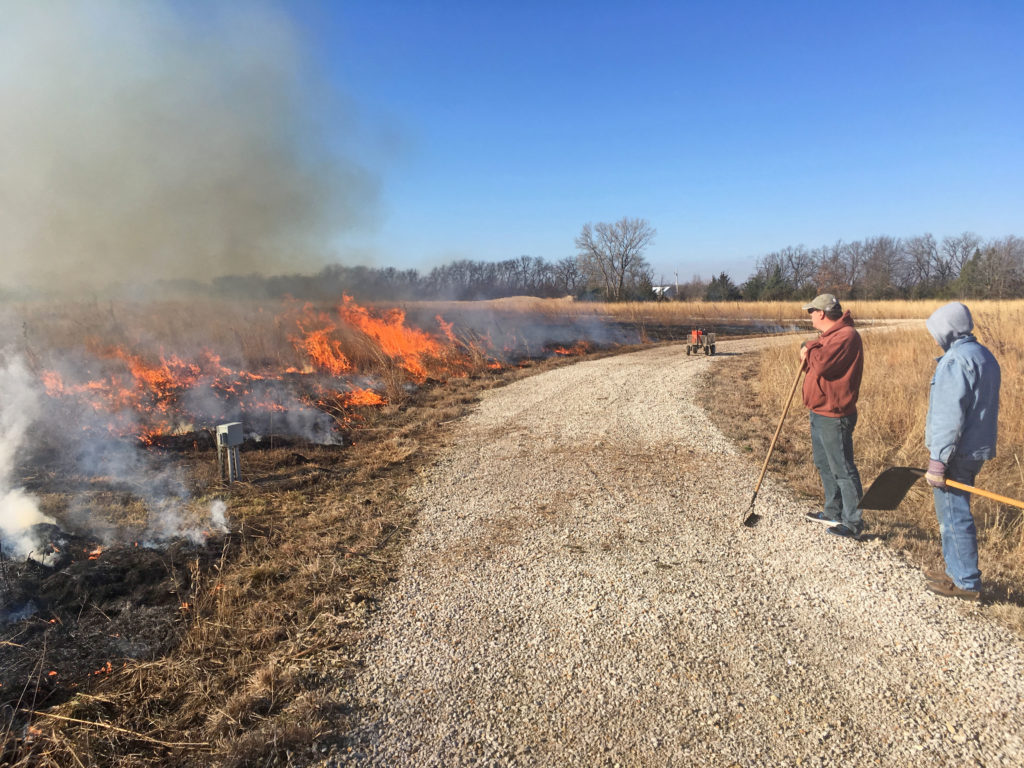
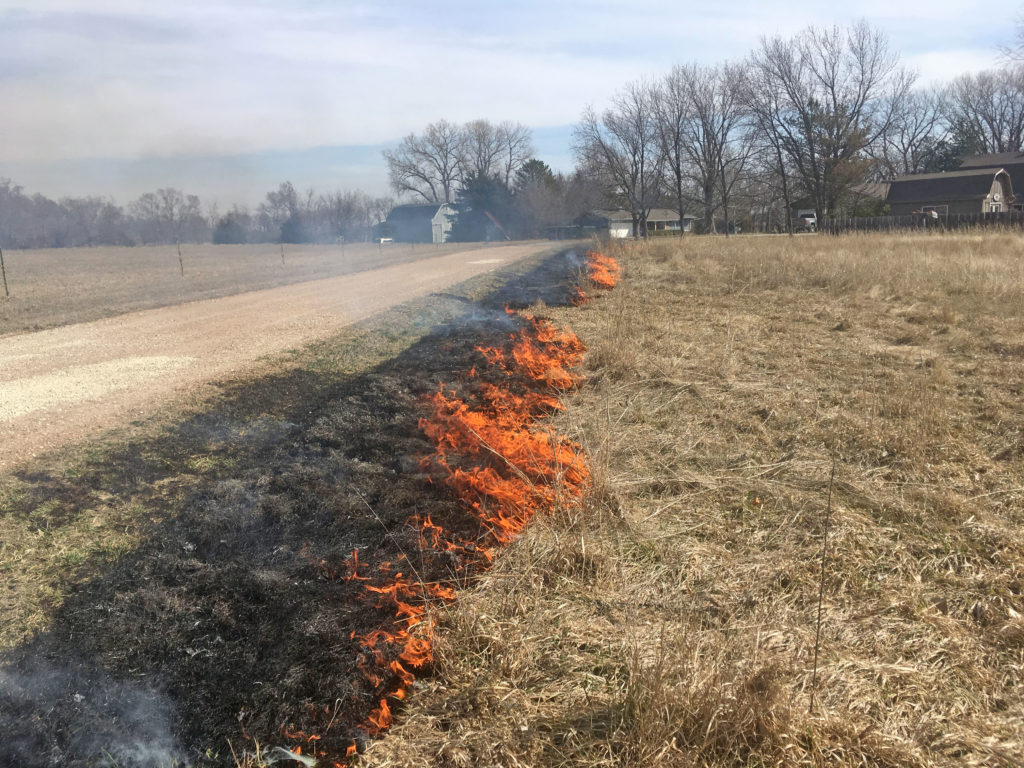
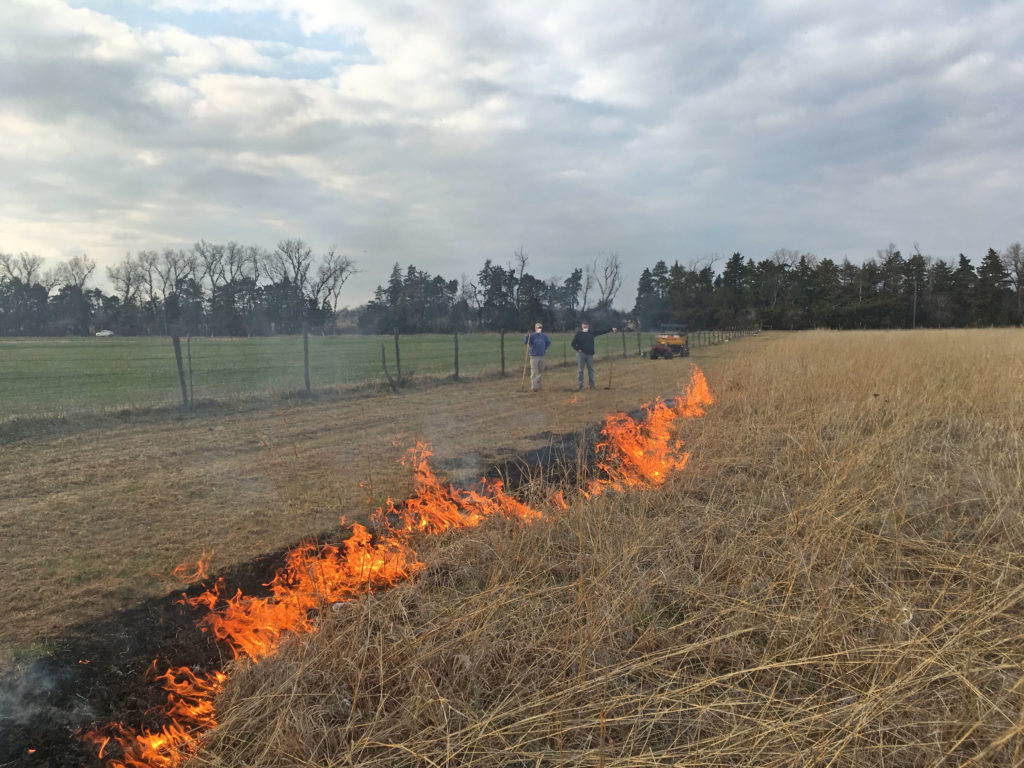
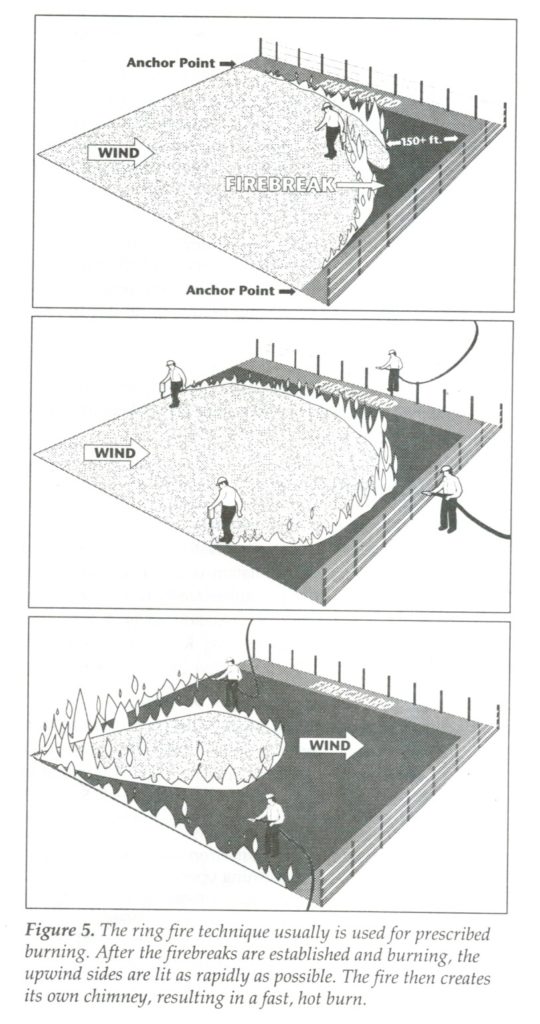
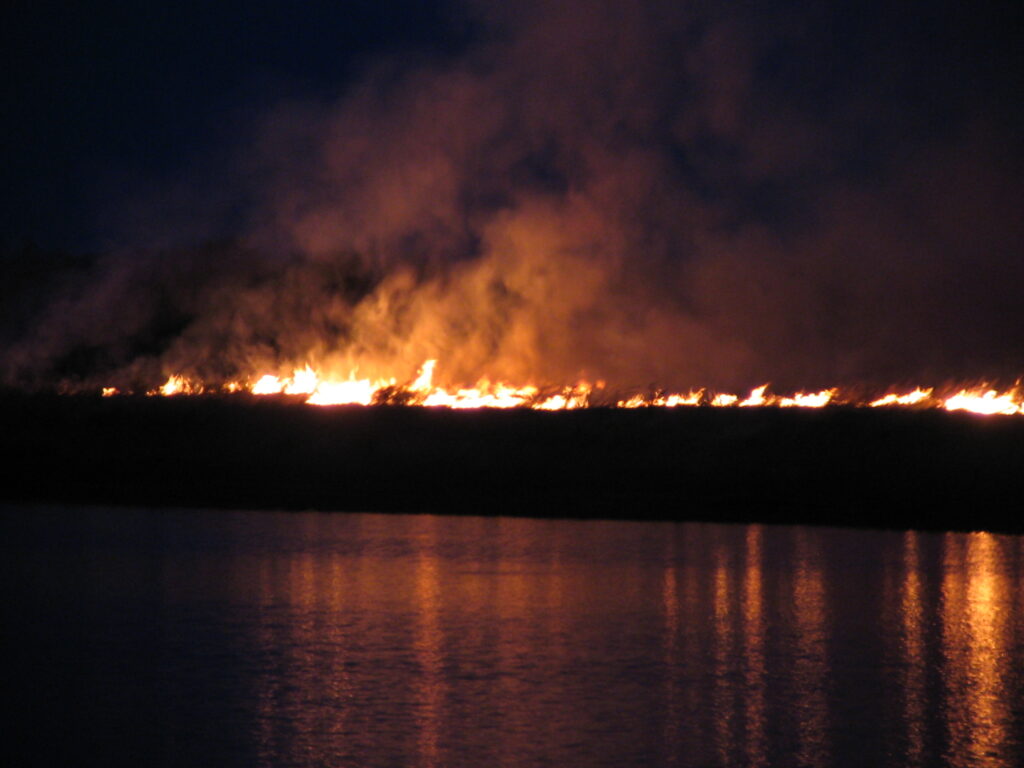
They were able to open up the upland areas where they had successfully removed mature trees and restore contiguous areas of grass and wildflower-dominated prairie. In these areas, the Schwabs implemented a regular rotation of mowing and prescribed burning to control any further invasion of woody plants. They networked with a local fire department to help them do this. They found mowing and burning to be much less labor-intensive than manual tree removal and effective tools for long term tree management.
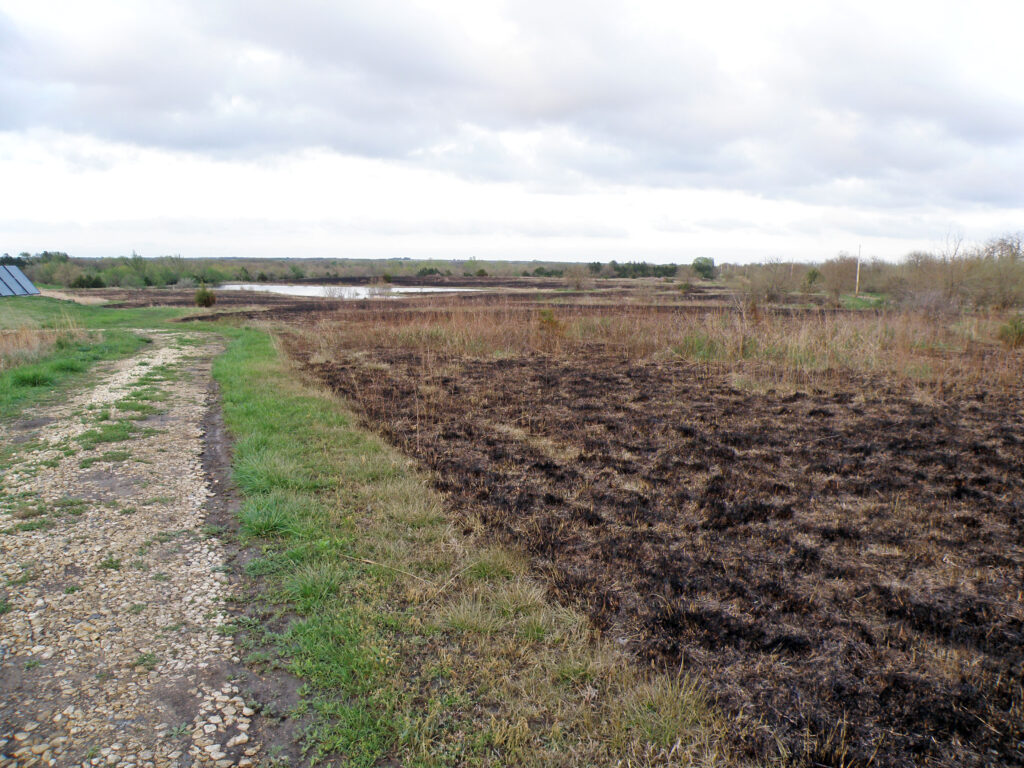

Carolyn and Terry have made great improvements in restoring the prairie and emergent wetlands with tree management, but they know that they cannot rest on their laurels. Mature, seed-producing trees on their land and neighboring properties make keeping up with tree invasion a continual challenge. In addition to maintaining a routine of mowing and burning, they continue to cut and treat a number of invading tree species including honey locust, Bradford pear, Osage orange, Siberian elm, eastern red cedar, and the shrub Japanese honeysuckle. They are also on the lookout for the highly invasive, noxious weed sericea lespedeza which is becoming increasingly present in the area.

Wildlife Monitoring
Carolyn invests a great deal of time monitoring and reporting on the biodiversity observed on their property. Daily walks to document bird populations, track phenology of flowering plants, and photograph butterflies are all part of what she sees as being an informed land steward.
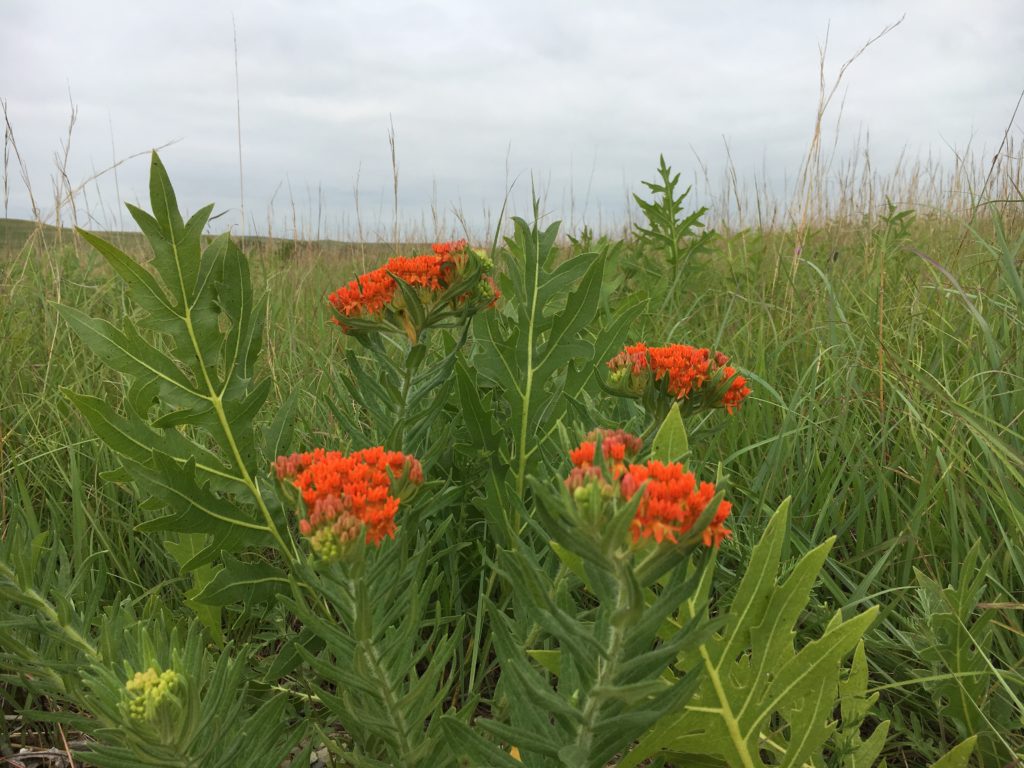
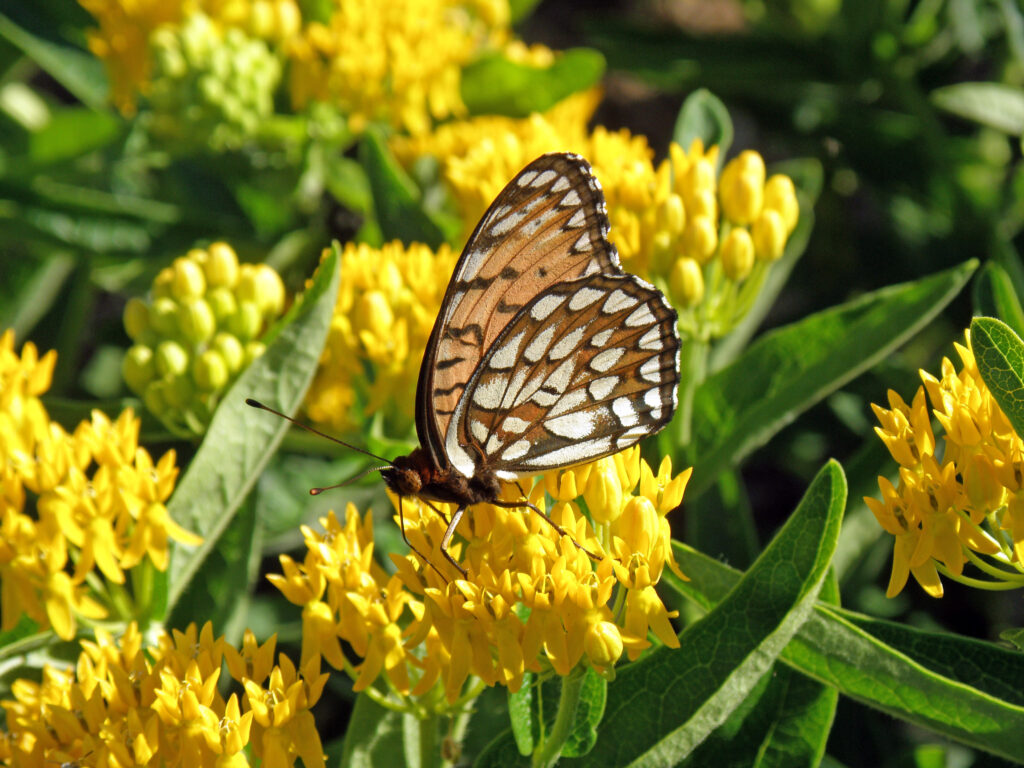
Regal fritillary butterflies are dependent on habitat including diverse, large tracts of prairie. Even though the Schwabs have been improving the habitat of their prairie, regal fritillary numbers seem to be declining in recent years on a landscape scale. Carolyn has been planting nectar plants like butterfly milkweed and regal fritillary host plants (prairie violets) in the landscaping around her house to try and further support regal fritillary numbers.

Carolyn is a top-notch birder. According to the Kansas Bird Listserv Database, a total of 329 species of birds have ever been documented as observed in Harvey County. Carolyn has seen more of these species (270) than anybody. And with easy access to 109 acres of prairie, wetland, woodland, and open water habitat, Carolyn has seen a whopping 232 of these species on her property!
A favorite experience of hers was witnessing a rare event on October 27, 2010. Eastern Harvey County is well east of the main sandhill crane migration flyway and seeing cranes there is not common. That night, however, the Schwabs observed 200+ sandhill cranes settle in for the night at their pond and enjoyed hearing their calls through the night. The cranes took off the next morning, but left behind a lasting memory for Carolyn.
Return of Butterfly Milkweed
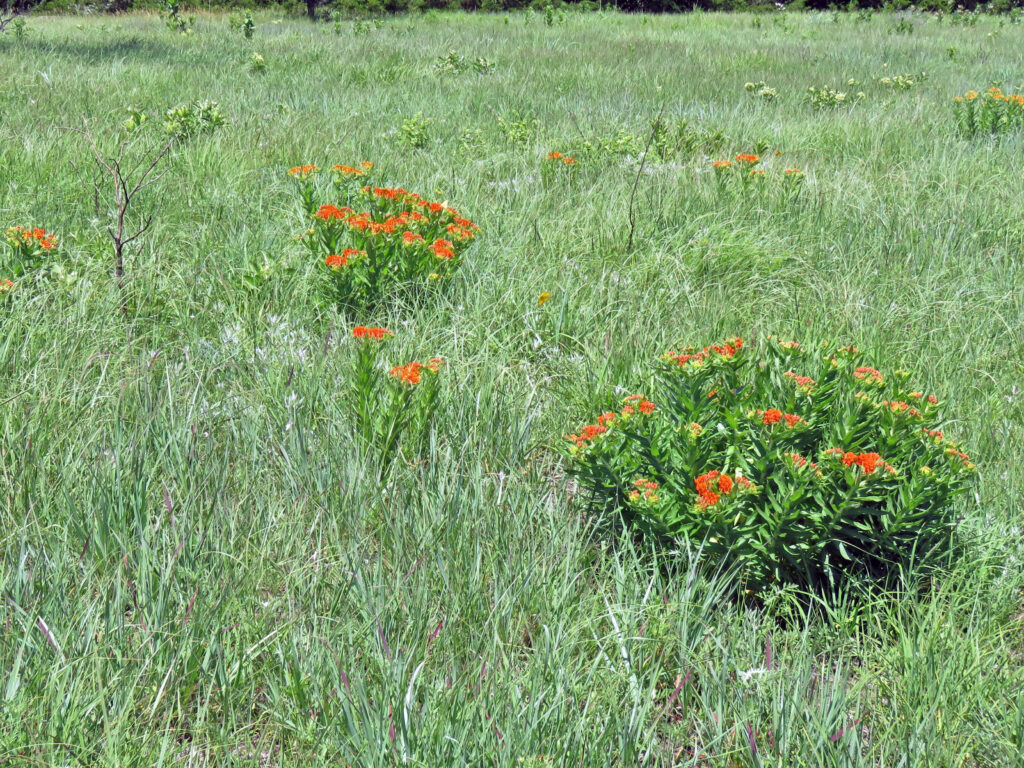
The Schwab prairie restoration efforts are not only increasing the presence of grassland bird populations, but plant diversity as well. For years, they have not seen any butterfly milkweed on their property. But during the growing season of 2020, Carolyn reports that she has seen 20 plants.

Protection for the Future
The Schwabs are considering registering their property with the Kansas Land Trust to protect this native prairie in perpetuity. By establishing a conservation easement on the property, Terry and Carolyn would be establishing guidelines for future landowners to follow that would help protect the prairie, watershed, and the diversity of species therein.
Thank you, Carolyn and Terry for your important prairie restoration land stewardship and for being willing to share your story.