I recently read an interesting article about monarch butterflies and their migration needs. The foundation of any successful monarch migration rests on a sufficient supply of native milkweeds, as these are the only plants monarch caterpillars can eat. However, there is ongoing research that suggests nectar plants besides milkweeds should receive more attention, since many milkweeds are done blooming when monarchs return to Mexico in the fall.
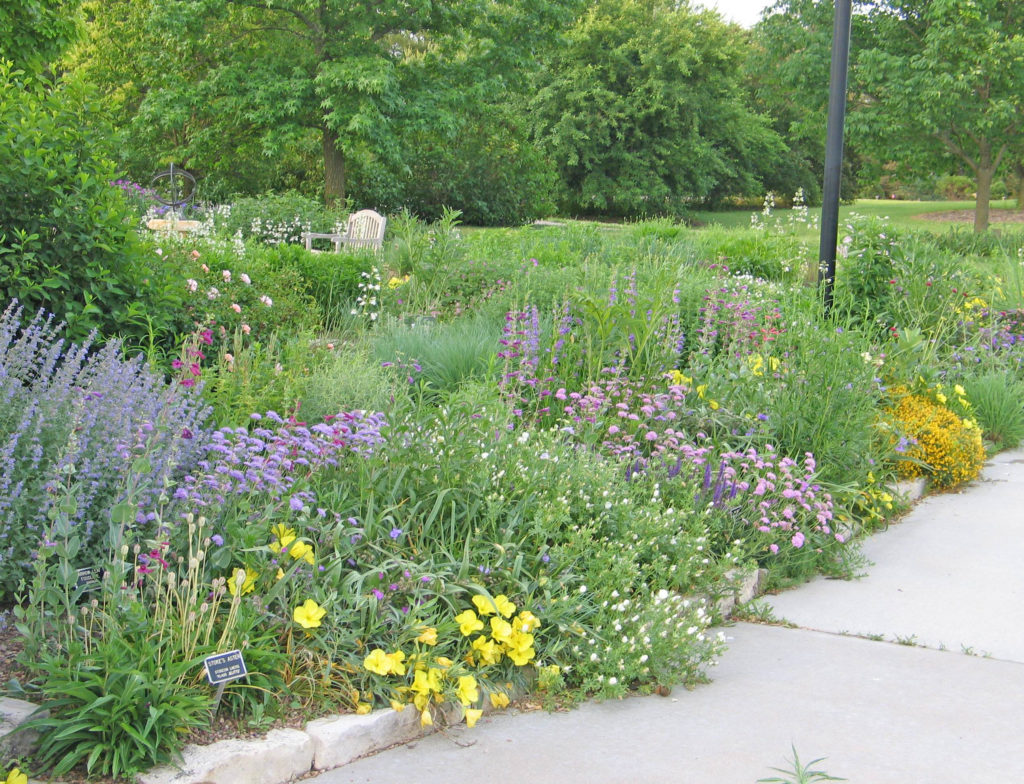
Adult monarchs are generalist feeders, and they need varied nectar sources. This is why succession of bloom within your garden is so important. A variety of beautiful wildflowers provide food for monarchs throughout the year, but also support many other butterflies, bees, birds and other wildlife. Yes, milkweeds are still critical to include in your design since they are both a host plant and a nectar source. But here are some other plants that will assist monarchs as they migrate:
Trees and Shrubs
- Ceanothus americanus/herbaceous (New Jersey Tea) – Attractive clusters of white flowers in spring and early summer.
- Cephalanthus occidentalis (buttonbush) – Interesting white flowers May-September and beautiful fall color. Likes moisture and is great for heavy clay soils.
- Prunus serotina (Black Cherry) – Long clusters of fragrant white flowers in spring. Large tree with fruit for birds later in the season.
- Rhus spp. (sumac) – Shrubs or small trees with useful flowers for pollinators, fruit for other wildlife and good fall color.
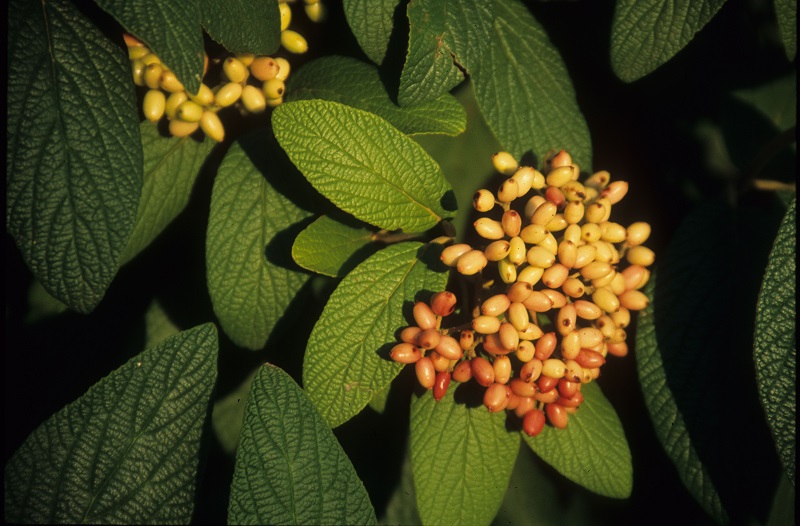
- Heptacodium miconioides (Seven-son Flower) – Small ornamental tree with flowers in September. Monarchs have flocked to our trees while in bloom.
- Sambucus canadensis (Elderberry) – Creamy white flowers in the summer atop this large wetland shrub.
- Lindera benzoin (Spicebush) – Yellow-green flowers in the early spring. Shrub with fragrant foliage and nice yellow fall color.
- Ribes odoratum (Clove Currant) – Bright yellow spicy scented flowers in April-May, followed by delicious black berries. It makes a nice understory shrub.
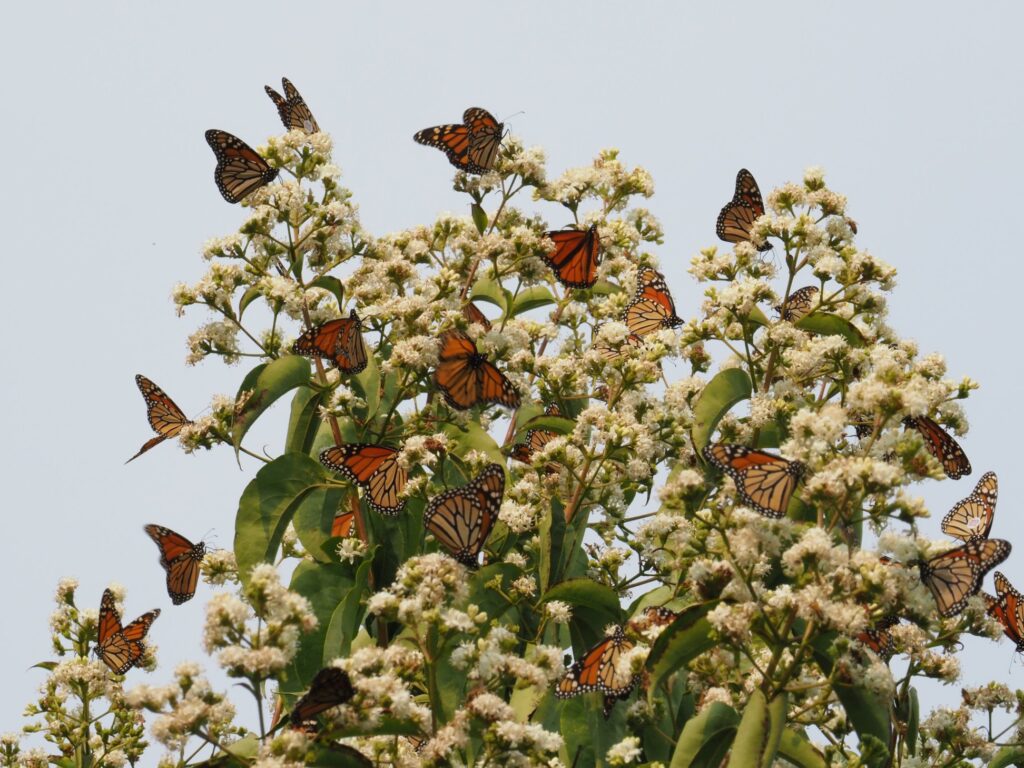

Perennials other than Milkweeds
- Symphyotrichum novae-angliae (New England Aster) – Purple, pink and lavender blooms September and October are extremely important nectar sources for adult monarchs.
- Other Aster species: Aromatic Aster, Sky blue Aster, and Heath Aster
- Solidago sp. (Goldenrod sp.) – Bright yellow blooms in the late summer through early fall.
- Vernonia lettermanii ‘Iron Butterfly’ (Ironweed) – Deep purple blooms in August and September.
- Liatris sp. (Blazing Star) – Purple blooms on these diverse native perennials are a favorite of pollinators.
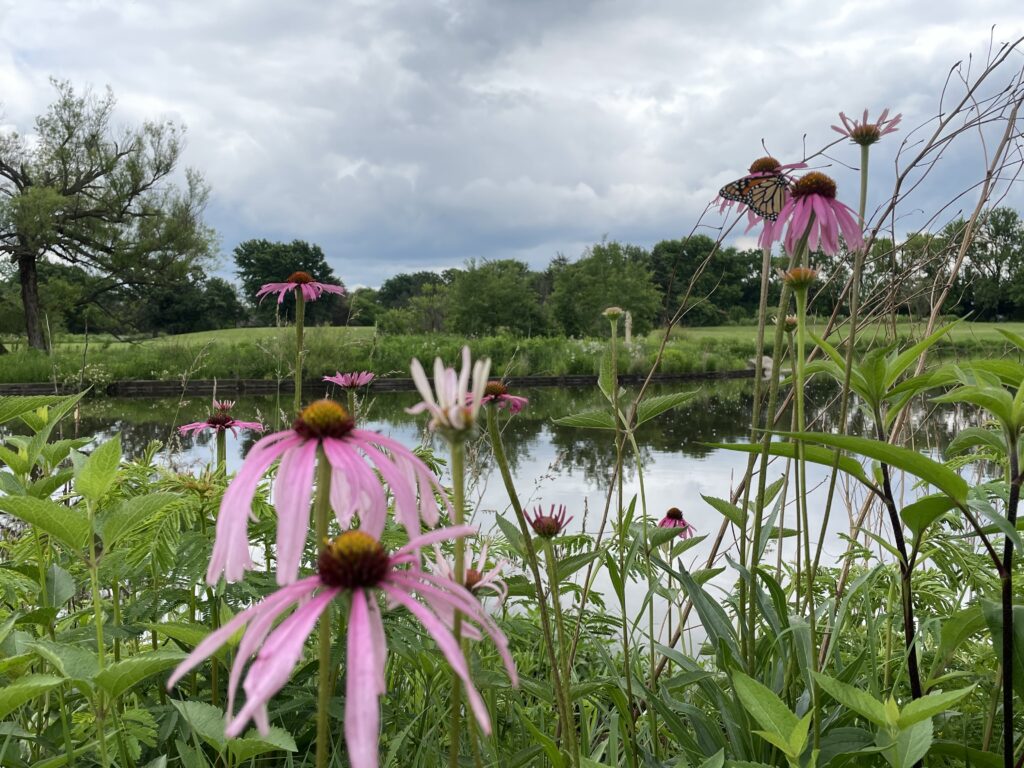
- Echinacea sp. (Coneflowers) – These summer blooming wildflowers provide a perfect landing pad for monarchs and pollinators of all sorts. The seeds are eaten by birds through the winter.
- Pycnanthemum sp. Mountain Mint – These spreading wildflowers are usually covered with pollinators of all kinds when they bloom in the summer. Give them room in the garden because they do roam.
- Monarda sp. (Beebalm) – Fragrant foliage and bright pinkish blooms attract a host of pollinators.
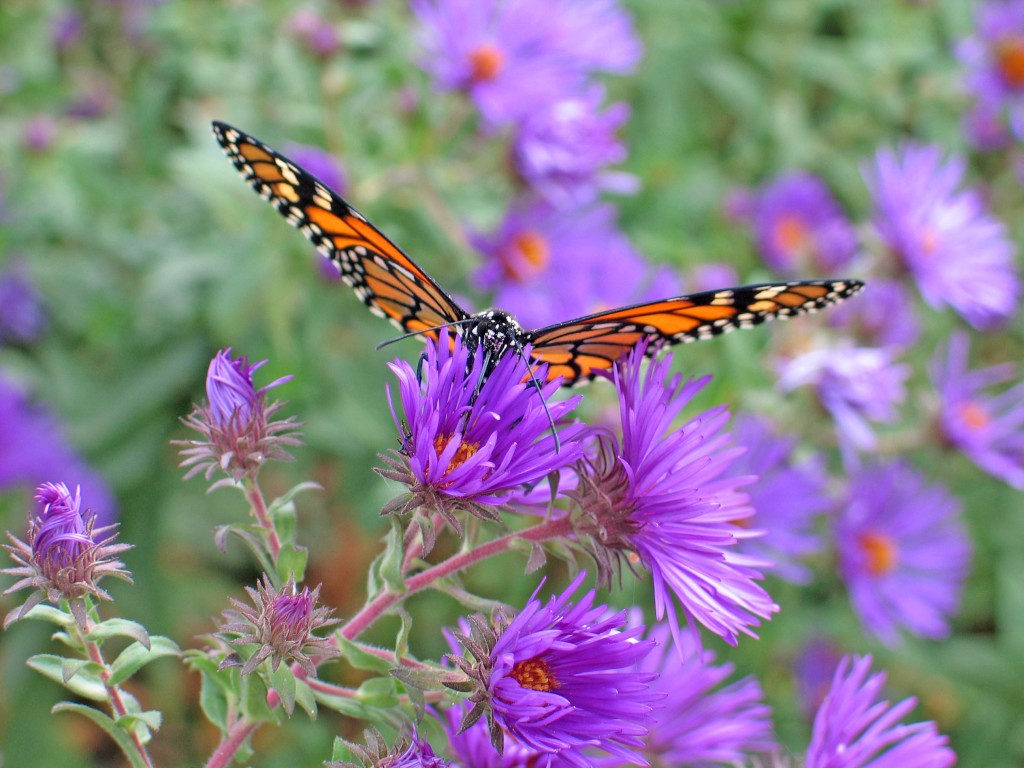
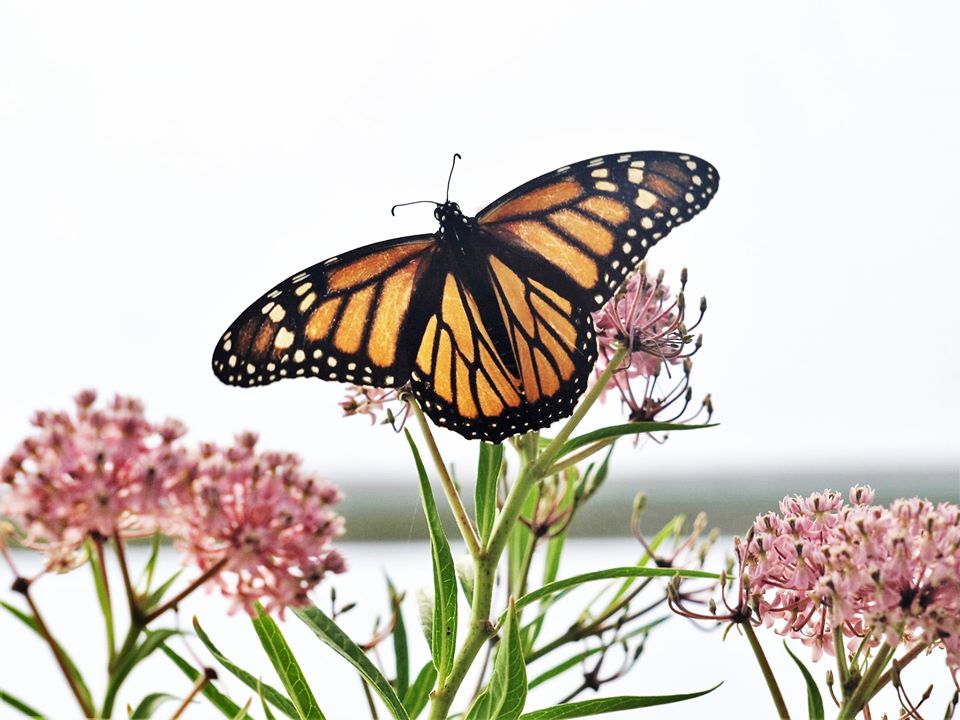


Fuel for the Flight
Again, monarchs need milkweeds. These plants are vital to their reproductive processes. However, they need other nectar-rich wildflowers too. This is one of the weak points in their return migration journey. As they migrate south in the fall, they are not reproductive. Their goal during this part of the migratory cycle is to fuel up on late season nectar plants and build up their body fat so they can make it to Mexico and survive the winter. There, in early March of the following spring, they will leave their mountain roosts to mate, lay eggs on milkweed, and start the cycle all over again.
It is so important to provide fuel and sustenance for Monarchs and other pollinators. Available milkweeds, nectar plants, along with water, trees or other protection at night for roosting and connected habitats will help them all along the way – south to north and back again.