The longest days of late June in Southcentral Kansas for me feel synonymous with sweltering hot swimming weather, carefree kids riding bikes, backyard BBQs, blooming milkweeds, butterflies, and the first signs of the fireflies of summer.
Saturday evening, June 12, 2021, I saw the first flash of a firefly in my backyard. I found many adult fireflies on the underside of milkweed leaves while looking for monarch caterpillars in my prairie garden. Over the last week, fireflies have begun putting on a dazzling light show in the early evening hours.
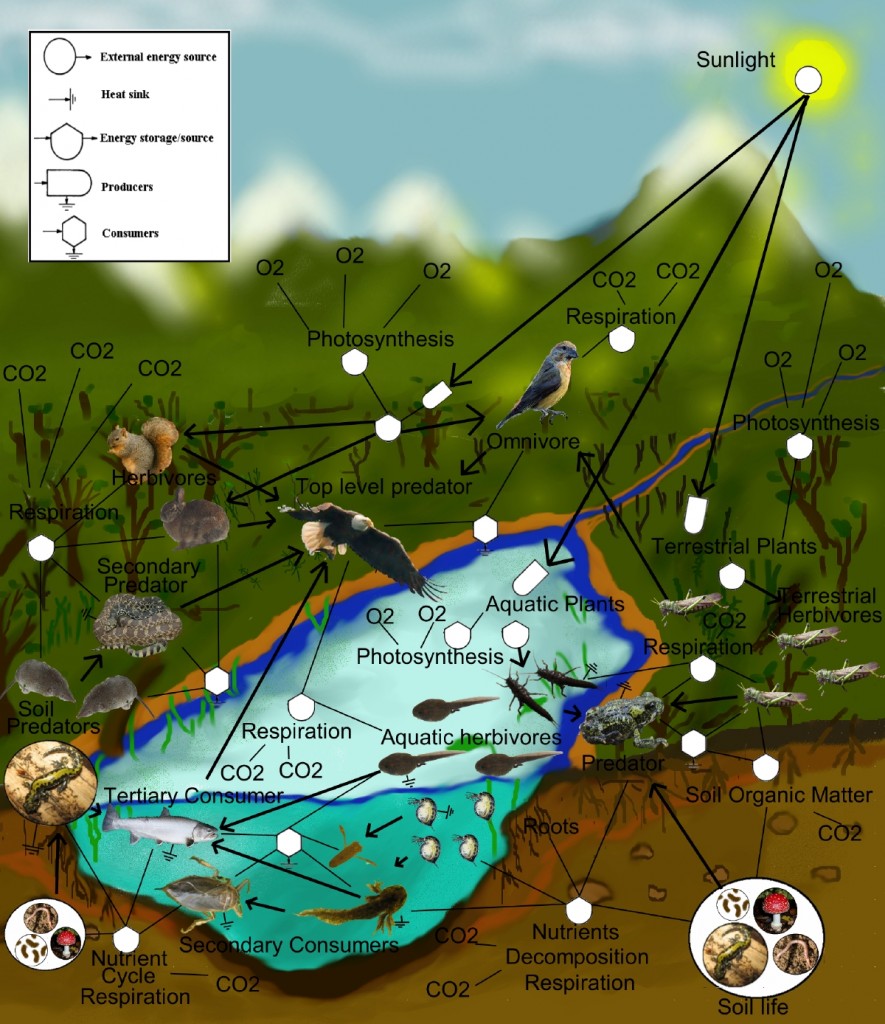
Firefly Diversity, Life Cycle, and Habit
Fireflies, sometimes referred to as lightning bugs, are neither flies nor bugs. They are beetles (order Coleoptera) in the family Lampyridae. Nearly 170 firefly species of Lampyrids have been documented throughout the United States and Canada.
Like all beetles, fireflies go through complete metamorphosis in four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. The complete life cycle can range from two months to three years or more, the majority of the life cycle spent in the larval stage. The larva is a predator that eats soft-bodied invertebrates including earthworms, slugs, and snails. It first injects paralyzing neurotoxins to immobilize its prey. Then it secretes digestive enzymes to liquify it for easy consumption.
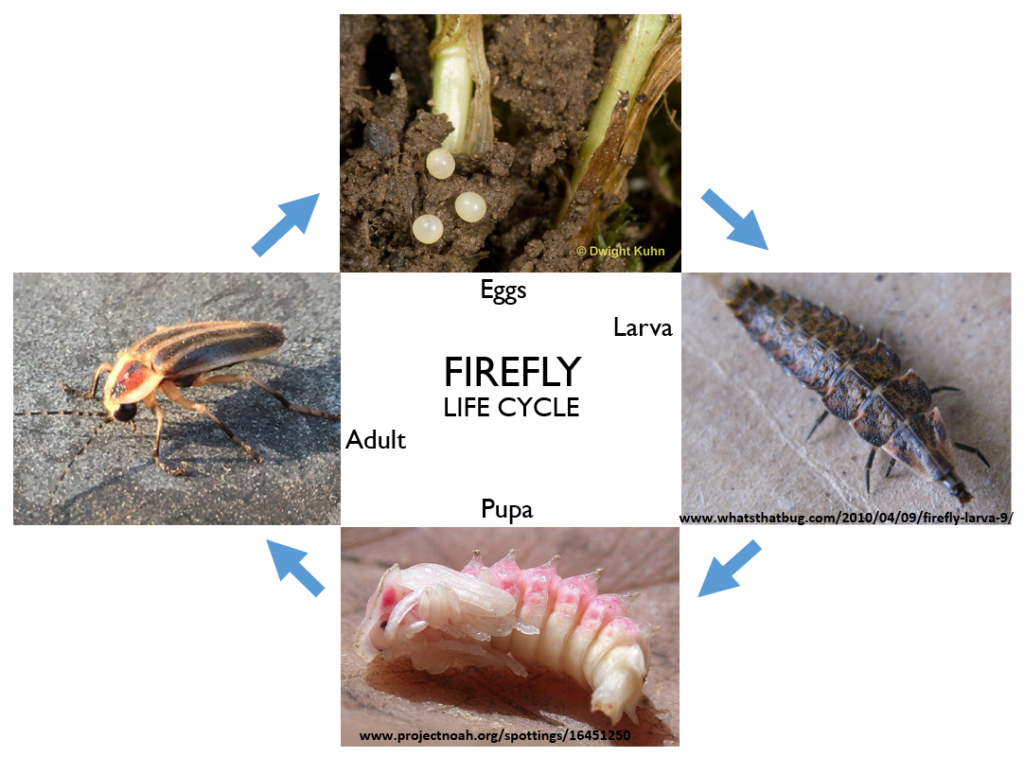
Fireflies have specialized light organs under their abdomens that produce the compound luciferin. Luciferin combined with oxygen undergoes a chemical reaction known as bioluminescence that produces light with almost no heat. Even the eggs and larvae of some species glow, hence the name “glow worm”. Adult males and females turn that light on and off to communicate in their mating ritual. Each species of firefly has its own distinct lighting pattern.
Research shows that this illumination system also deters predators. Just like a monarch butterfly has a bright coloration system to communicate that it is poisonous, fireflies send the message that their bodies are toxic by flashing. I have big brown bats living in my yard. I thought they would easily munch on fireflies since beetles are a favorite part of their diet, but this article helped me to learn otherwise.
Larry Buschman – Local Firefly Expert
I probably would not have become inspired to learn more about fireflies if it hadn’t been for meeting Larry Buschman. Larry is a total firefly nerd and a knowledgeable one at that. He travels throughout the Central United States every summer to look for and study different species of Lampyrids. Larry was kind enough to let me tag along last summer and observe him in action. When I met him for the first time in a parking lot along the Walnut River near El Dorado, he wasn’t hard to spot. With his red light head lamp, insect net, and his homemade contraption consisting of a “flashing system” and camera on a fishing pole to lure in and photograph various species, Larry looked like a character out of Ghostbusters. I knew right away I had met a new friend.
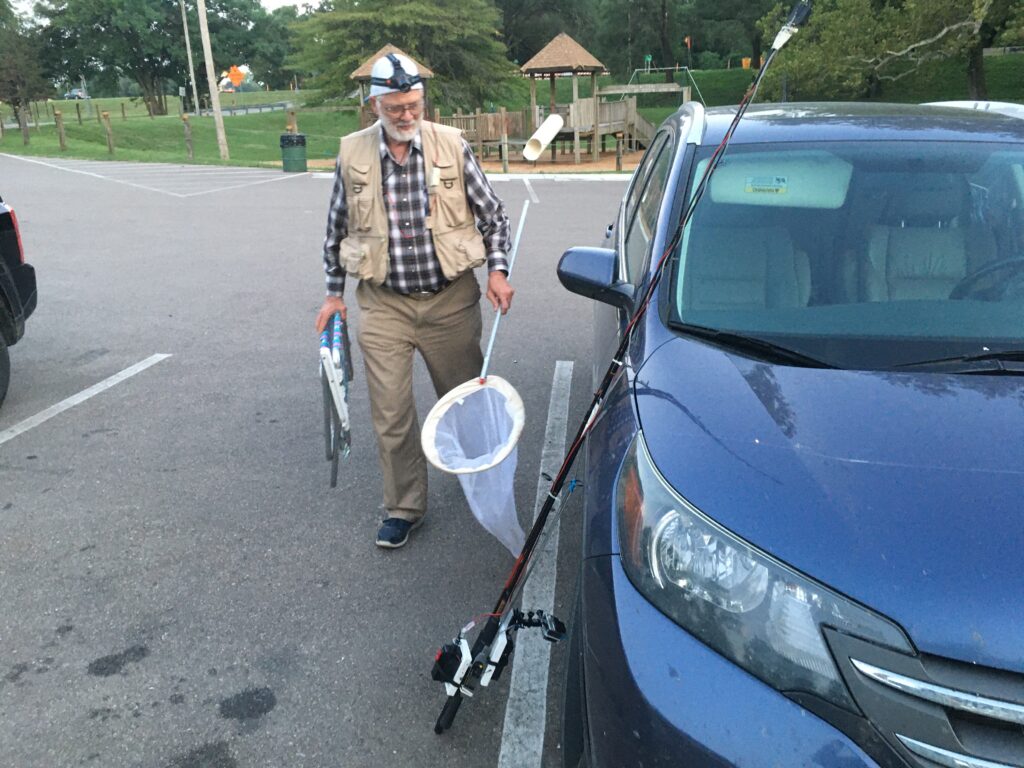
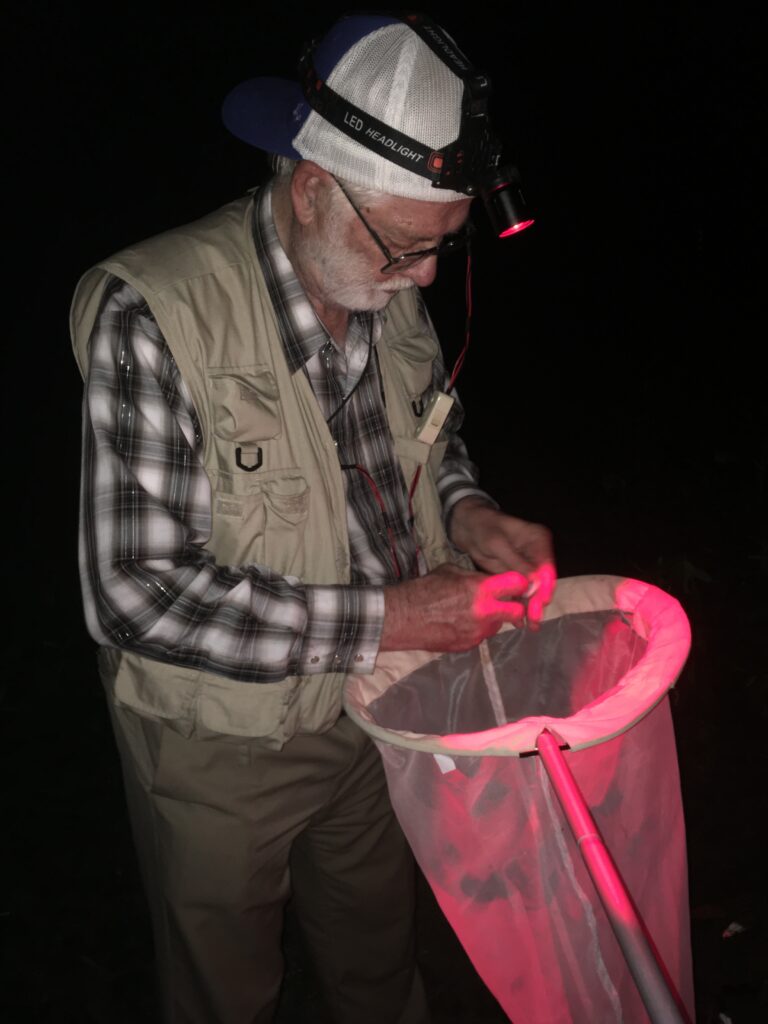


We set out for the deepest and darkest part of the riparian woods. As it got dark and Larry got to work luring in fireflies, we caught two different species of fireflies. We found Photinus pyralis “The Big Dipper” abundantly. This is the species that you and I probably most commonly see in our yards in Kansas. The males display five 1-2 second flashes regularly every 4-5 seconds, which elicits a similar one-time flash by the female.
We also found a less common species in the genus Photuris. This group is easily identified by its humped back and longer legs. Female adults of Photuris are often predators of other fireflies. While the long, slow flash narrows down the identification of this firefly to one of a couple of different species of Photuris (either P. caeruluscens or P. lucicrescens), Larry was not sure on the identification. So, for now it gets the more generic designation of Photuris spp. See more details about the firefly species of Kansas in Larry’s Field Guide to Western North American Fireflies.
Firefly Threats and Conservation
World Firefly Day is coming July 3-4, 2021 and marks a good time to think about their conservation. Firefly species around the world are threatened. A recent study identified that the three most prominent threats to fireflies are 1) habitat loss, 2) artificial light, and 3) pesticide use. Artificial light at night and pesticide use are two threats that we can curtail fairly easily and with minimal effort. Check out light pollution solutions and firefly-friendly lighting practices to help you reduce light pollution in your landscape. And consider the sensible approach of Green Scaping to reduce and even eliminate pesticide use in your landscape.
Addressing the largest threat to fireflies of habitat loss is one we can also take on in our landscaping. It is a drumbeat that we deliver regularly through our education channels at Dyck Arboretum. Building habitat for insects in general will benefit any subgroup of insects including fireflies. Plain and simple, you can do this by increasing the diversity of native plants in your landscape.
For further firefly conservation recommendations, check out the Xerces Society’s comprehensive publication Conserving the Jewels of the Night.
I’ll leave you with a favorite children’s book to share. Children will be an important part of firefly and insect conservation into the future. Consider how you might restore insect habitat, curb pesticide use, and reduce light population to help protect the fireflies of summer.