Schizachyrium scoparium, also known as little bluestem, is the official state grass of Kansas. And for good reason! It is found in every county of Kansas, produces an incredible amount of biomass per acre, and is host to nine species of skipper butterflies. No fertilizer or fuss required, it will grow well in harsh conditions and poor soil. Little bluestem is a great grass to add to your landscape if you want something ecologically beneficial, water-wise, and colorful.
Variety vs Species
Because it is such an impressive plant, little bluestem has gotten a lot of attention from the horticultural industry. Professional breeders have selected and cultivated many new varieties. Humans have been selecting and breeding desirable traits into plants for thousands of years, so we are getting quite good at it by now. Customers looking to buy little bluestem have a lot of options to choose from in terms of height, habit, and color palette. While they are all still S. scoparium, they all offer something different that might benefit a certain landscape use. Below is a comparison of several options and their traits to help you decide.
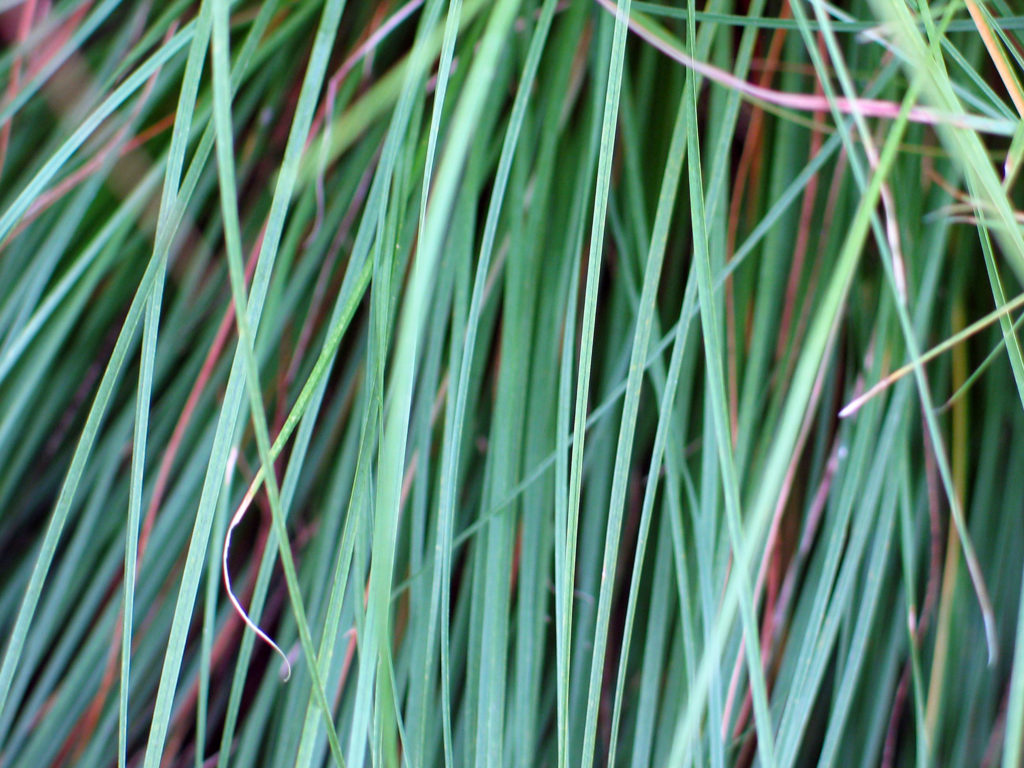

S. scoparium
The straight species, as we say, is the regular old wild type. S. scoparium that’s propagated by seed is genetically diverse from every other little bluestem growing around it. In contrast, most cultivated (named) varieties are propagated by division, meaning they are exact genetic copies of each other. This ensures the same coloration and habit. But if you don’t need that kind of aesthetic assurance, the classic little bluestem is a great option. You’d find this growing in prairies, pastures, and field edges. Pros: genetic diversity, great for restorations, wildlife areas or pastures, usually cheaper than branded varieties. Cons: floppy, not as colorful as other options, height is less predictable.
‘Jazz’ Little Bluestem
Foliage height: 1.5 to 2 ft
Total with bloom: 2.5 ft
One of the main differences between bluestem cultivars is height. ‘Jazz’ is a great solution for folks who want bluestem, but need it to be shorter than the regular species. A variety brought to market by Intrinsic Perennials, ‘Jazz’ usually stays under 24 inches and has a very bushy, upright habit. Pros: short, full and fluffy, upright. Cons: not as colorful as other options
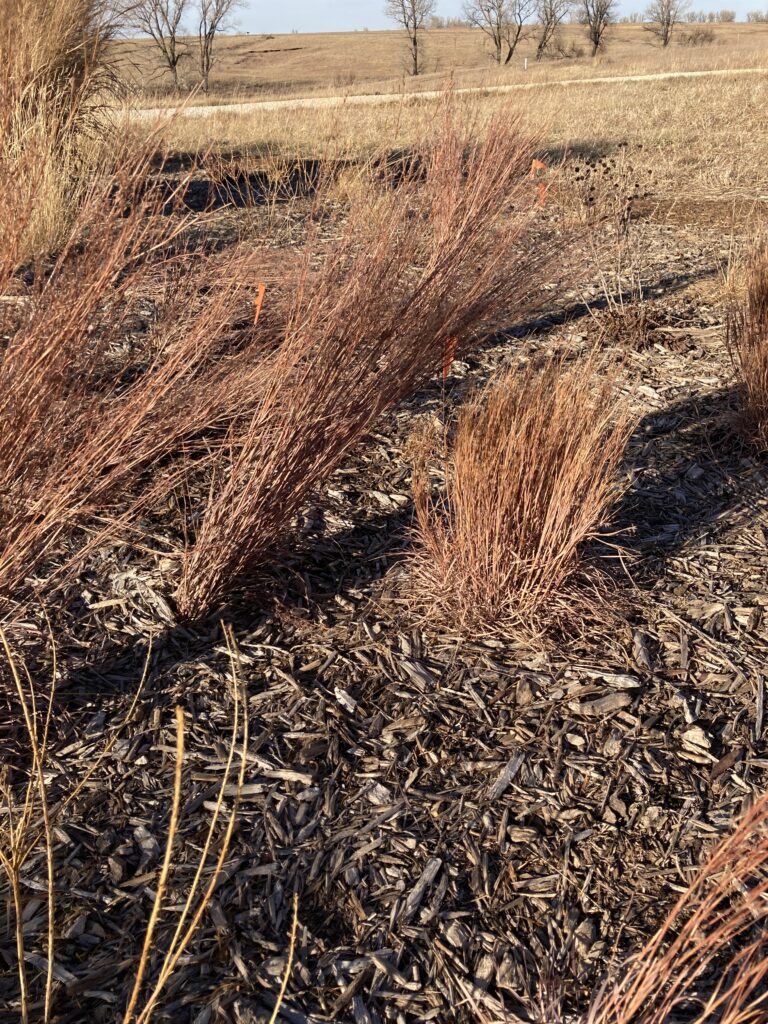

‘Twilight Zone’ Little Bluestem
Foliage height: 2 ft
Total with blooms: 4 ft
Known for its incredible coloration, ‘Twilight Zone’ is a fan favorite. Year after year we sell out of this one, and even our suppliers can’t keep it in stock. It has a powder blue coloration on the grass blades, followed by deep purple tips in fall. Mid-height, it is not as tidy and compact as Jazz but still stands up well with minimal floppiness given the right conditions. Pros: unbeatable blue color. Cons: too tall for some applications, may flop if partially shaded or in rich soil.

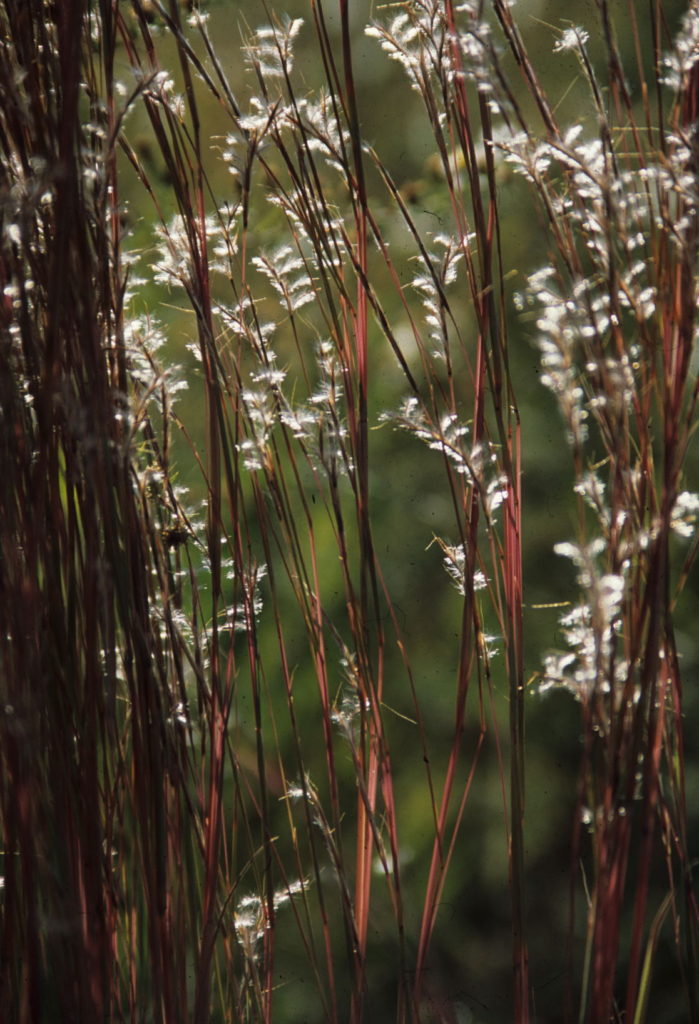
‘Blaze’ Little Bluestem
Foliage height: 2 ft
Total with blooms: 3 ft
If you like red, ‘Blaze’ is the choice. This variety is lush and green all summer, then packs a punch in fall with its deep red/orange/pink tones that delight all winter. ‘Blaze’ was actually bred as a high-yield pasture grass in the 1960s, but has been lauded for landscape use because of its beauty. ‘Blaze’ is especially nice in mass plantings. Pros: red fall and winter color, vigorous growth. Cons: flops easily if soil is too rich

I could go on and on about other favorites like ‘Standing Ovation’, ‘Prairie Blues’ and ‘Carousel’. No matter which little bluestem you choose, it will be a great low maintenance plant providing habitat and beauty all year long.