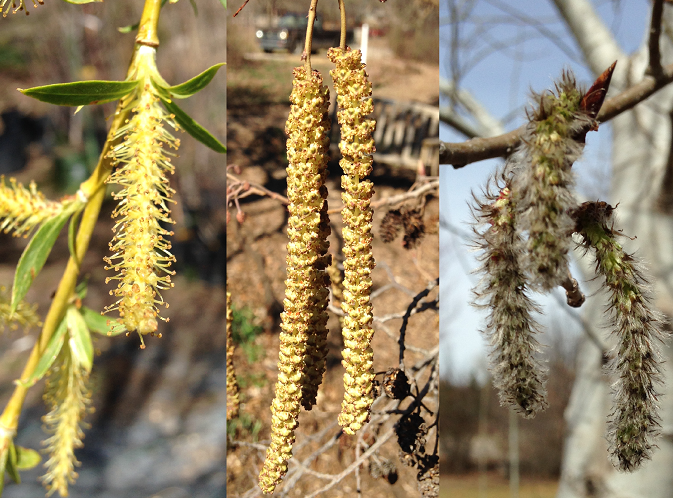
Sneezing, coughing, watery eyes – everyone is complaining about allergies this time of year, the Arboretum staff included. Many people point the blame at any pretty flower they see in early spring, such as Bradford Pear blossoms (Pyrus sp.), redbuds (Cercis sp.) or daffodils (Narcissus sp.). But it is likely to be less obvious blooms causing your sniffles – catkins. The trees are chalk full of these inconspicuous, pollen-spraying fiends! I’ll have to put aside my animosity for them and their disastrous effect on my sinuses while I explain their fascinating botany…but I’ll have to blow my nose first.
Structure and Function
Catkins are flowers adapted to be pollinated by wind, which is known as anemochory. (Pollinated in water? Hydrocory. Pollinated by birds? Ornithochory. You get the idea.) Their dangling habit is part of this adaptation, and pollen is released from male flowers when wind causes them to shake. These worm-like blooms are actually hundreds of tiny flowers strung together. Each catkin is either male or female, but both sexes may or may not be carried on the same plant. If a single plant produces both male and female catkins it is considered ‘monoecious’. Some tree and shrub species have separate sexes and produce only male or female flowers on a single plant, meaning they are ‘dioecious’.
No Beauty Queen
In general, the prettier the flower the less likely it is to be pollinated by wind. The striking white pear trees blooming now are mostly pollinated by bees, and therefore not the cause of wind-born pollen allergies. If the flower is colorful and attractive it is probably luring in winged creatures to carry it’s pollen becuase the grains are too heavy to be carried on the wind. Catkins are not burdened with the task of being beautiful – they don’t have to attract a subjective eye for pollination. But in the plant world, if you can’t be pretty then you must be prolific! These little flowers release enormous amounts of pollen onto the breeze, with little chance that any of it will serendipitously land on the female of the corresponding species. Not only does the pollen grain have to float its way to the opposite sex, but it must then land exactly on the tiny stigma, the pollen receptacle atop the female flower, to produce pollination. What a feat! With such slim odds, it is no wonder that these trees produce prodigious amounts of pollen, much to the dismay of allergy sufferers.
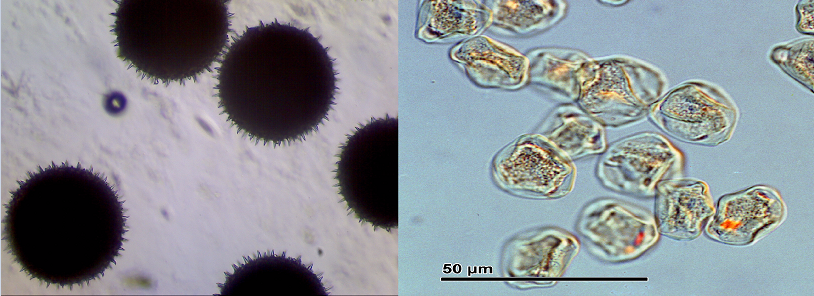
Left , ragweed pollen (Amrbosia) Right, Hazel pollen (Corylus). Hazel trees produce catkins. Ragweed does not have catkins, but the pollen is so annoying I thought everyone should know what it looks like.
Whether their pollen ends up in your nose and eyes, or the catkins themselves fall wet and soggy on your windshield, try not to loathe them too much – they are just another of nature’s incredibly well-designed survival mechanisms, and all your sneezing is just a sign that spring has arrived!
Attributions:
Wikimedia public domain images
Salix flowers – By Internet Archive Book Images [No restrictions], via Wikimedia Commons
https://archive.org/stream/textbookofstruct00thom/textbookofstruct00thom#page/376/mode/1up
Ambrosia pollen – By Nikita Karasik (Own work) [CC BY-SA 4.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)], via Wikimedia Commons
Corylus pollen – By Doc. RNDr. Josef Reischig, CSc. (Author’s archive) [CC BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons