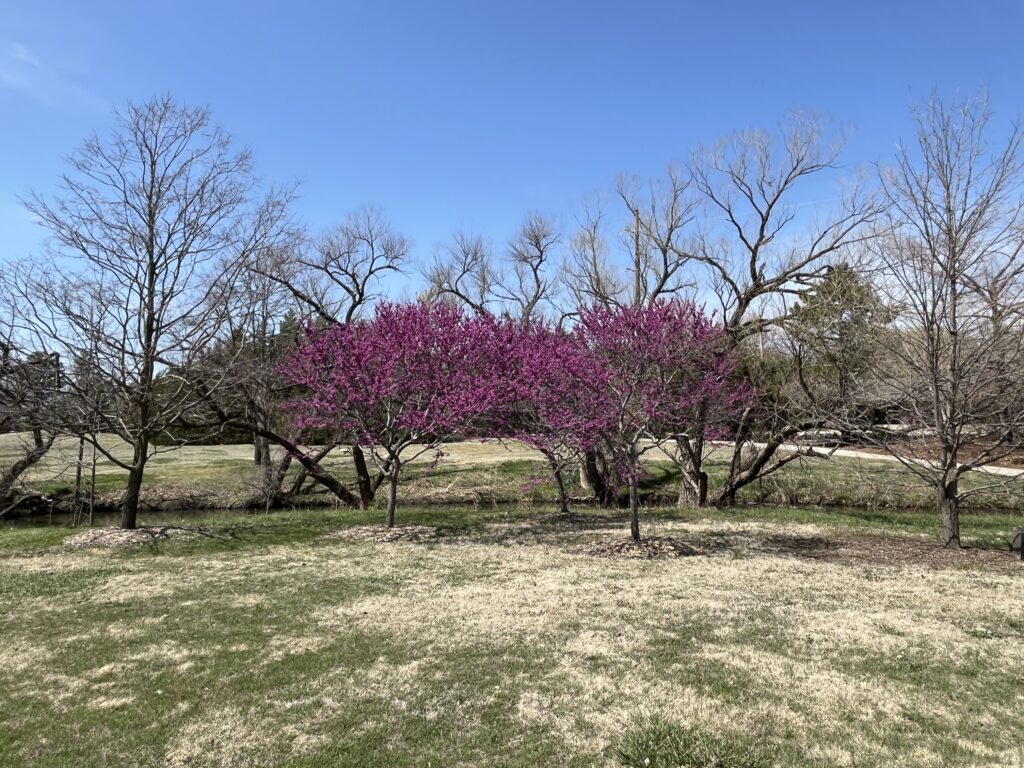
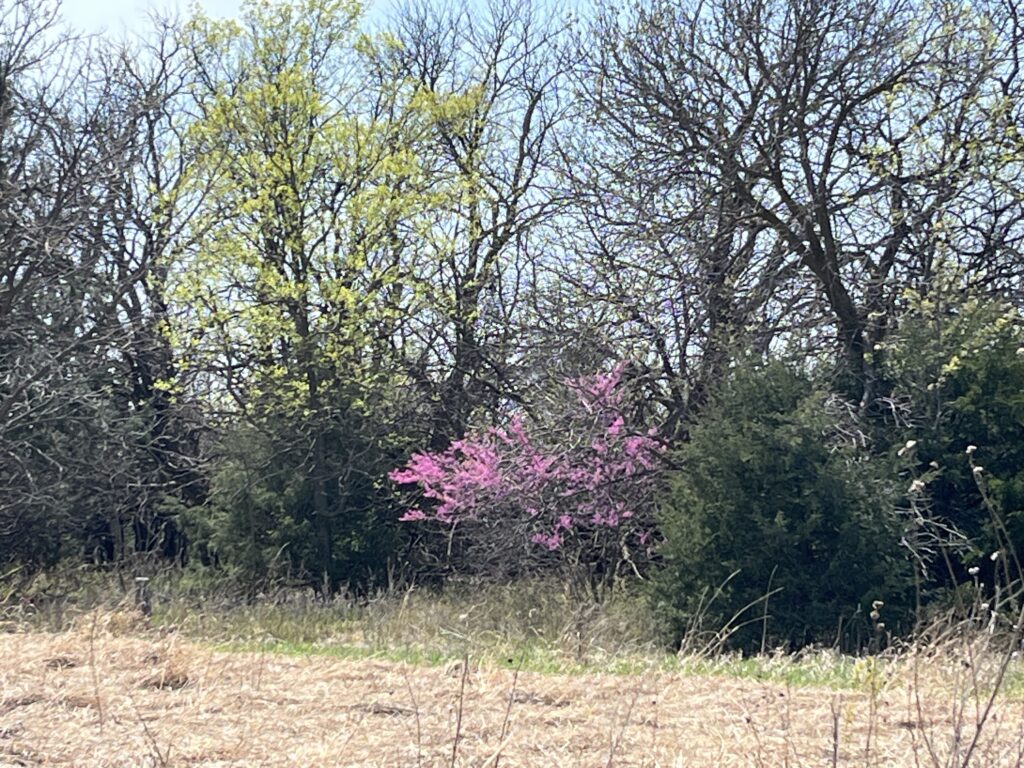
Have you noticed the redbud trees blooming this year? They have really been putting on quite a show. For some reason, they have really popped in the landscape this year. Maybe it’s because they are a stark contrast to the drab landscape that is slowly coming to life. Or maybe it’s because they are a native alternative to the ubiquitous and noxious Callery pear trees that are spreading everywhere. Anyway, take some time to admire this small native ornamental tree.

Benefits of Redbuds
The edible pink blooms are a favorite of many different pollinators in early spring. There are not many trees and shrubs blooming this time of year, so they rely on the flower nectar to keep them going. These early blossoms draw in nectar-seeking insects that are quickly plucked up by birds too. Northern bobwhite quail and a few songbirds, such as finches and chickadees, will eat the seed pods. It can be used for nesting sites and nesting materials, and it also provides shelter for birds and mammals.
In the wild, redbuds are commonly seen in tree margins and along swales and ravines. The small stature of the tree allows it to fit into most landscapes. Most trees develop a nice vase-shape that shows off the attractive reddish tan bark. The heart shaped leaves emerge as the flower clusters fade. In the fall, these leaves turn yellow and orange before dropping off before winter.
Growing an Eastern Redbud
With multiple seasons of interest, redbuds (Cercis canadensis) deserve a place in just about any landscape setting. Redbuds are hardy in zones 4 to 9 so they are adapted to our climate here in Kansas. New trees can be planted in the spring or fall with my preference being a fall planting.
This small ornamental tree is native to the eastern half of Kansas. It is one of the earliest trees to bloom and produces an abundance of purplish-pink flowers. For best growth, plant them as an understory tree with morning sun and afternoon shade. They can grow in full sun but prefer protection from the hot afternoon sun. In too much shade they are leggy and sparse. A moist soil is preferred, but they are quite drought tolerant once established.
We have seen our redbud foliage damaged by herbicide drift, some of our on doing but other times from farmer spray drift, so be cautious when using chemicals around your trees. Redbuds are in the legume family so they develop bean pods. These tan pods can sometimes be very abundant so keep that in mind when choosing a location. I have never seen this as a problem, but they will eventually fall from the tree.
Eastern Redbud Pruning and Maintenance
Redbud trees grow quickly, usually putting on a foot or two per year depending on their growing conditions. Typically, they live for about 30 to 40 years. Once established, most trees will only need to be watered during periods of prolonged drought. Mulch around the trunk with coarse wood chips will help the soil retain moisture and cool the root system. The gnarled trunks and branches can break from strong winds, so occasional pruning may be needed to thin out the canopy.
Besides breakage, redbuds are afflicted with cankers on the branches and stems. Usually, this is not a problem that is lethal. Most redbuds have some sort of raised bark that adds to the character of the tree. Also look for fungal problems like mildew, verticillium wilt, and leaf spots. These are more likely to occur when airflow is limited, so consider pruning your tree so it has a more open structure to provide better ventilation. Insects are not usually a problem, but webworms and Japanese beetles may appear and can be treated with an appropriate but cautious application of a recommended insecticide.
Top Eastern Redbud Cultivars
- Eastern Redbud (Cercis canadensis var. alba) (white flowers)
- ‘Forest Pansy’ and ‘Merlot’ have red/purple new growth. In my experience, these red leaf forms need more protection from the hottest afternoon sun.
- Oklahoma Redbud (Cercis canadensis var. texensis ‘Oklahoma’) Glossy green leaves, more intense flower color, insect resistance.
- Rising Sun Redbud-dwarf flowering tree (6-10 ft tall) has unique tri-colored leaves that blend sunny yellows and bright orange colors. This will need full sun protection as well.
- Ruby Falls Redbud-A petite, one-of-a-kind, cascading tree with maroon-purple to dark green leaves. Again, it will need to be protected from hot afternoon sun.